Hardware Reference
In-Depth Information
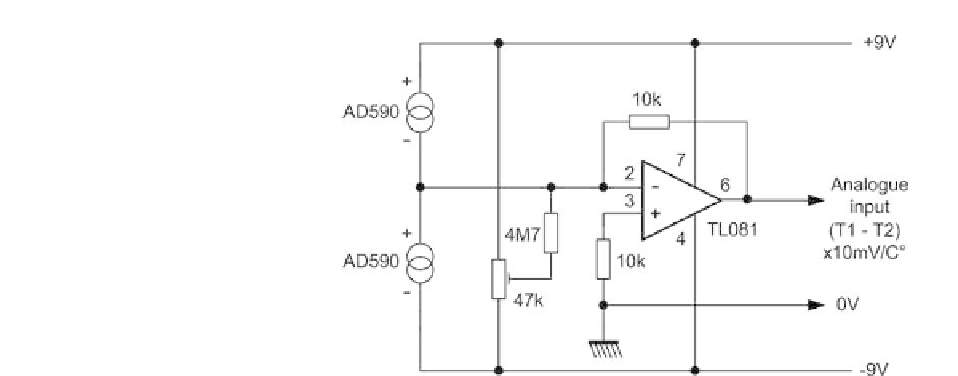
Figure 12.23
Arrangement of AD590 temperature sensors for differential
measurements
sensor is used to determine the actual air velocity produced. The sensor produces
an output of 0-10 V. The speed control thus requires an analogue input port and
an analogue output port. Both ports are to a full-scale range of 0-10 V.
The refrigeration unit is controlled with on/off digital control using a dedi-
cated I/O card and a comparator controlled from a DC 0 to 5 V control signal.
A temperature sensor is suspended in the airflow output from the refrigeration
unit and a signal (10 mV/
◦
C) is fed to a further analogue input port.
The pitch angle control uses a digital output port with a stepper motor (see
Chapter 9) and the spray bar control uses a single bit on a further digital output
port to provide simple on/off control.
Temperature sensing within the test section is based on a differential sensing
arrangement with pairs of AD590 temperature sensors (see Chapter 9). The
AD590 is well suited to this application as it offers excellent linearity (better
than
3
◦
C over the entire range) and the ability to operate well in remote sensing
applications with simple twisted-pair connections. Lead wire compensation
filters and circuits to ensure linearity are unnecessary with this type of sensor.
The output voltage from the differential sensing arrangement (see Figure
12.23) is 10 mV for every 1
◦
C difference in temperature. Hence an output of
100 mV will result from a temperature difference of 10
◦
C. Additional signal
gain is applied within the analogue input card.