Hardware Reference
In-Depth Information
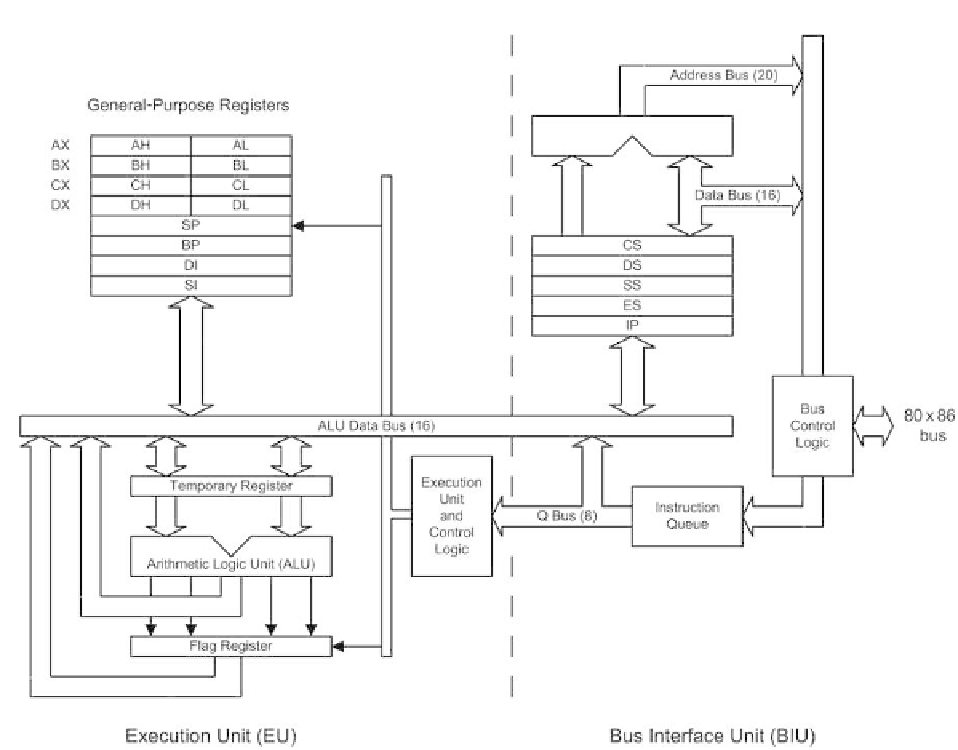
Figure 1.5
Internal architecture of the 8086
Addressing
The 8086 has 20 address lines and thus provides for a physical 1 MB mem-
ory address range (memory address locations 00000 to FFFFF hex.). The I/O
address range is 64 KB (I/O address locations 0000 to FFFF hex.).
The actual 20-bit physical memory address is formed by shifting the seg-
ment address four 0-bits to the left (adding four least significant bits), which
effectively multiplies the Segment Register contents by 16. The contents of the
Instruction Pointer (IP), Stack Pointer (SP), or other 16-bit memory reference
are then added to the result. This process is illustrated in Figure 1.6.
As an example of the process of forming a physical address reference,
Table 1.6 shows the state of the 8086 registers after the RESET signal is applied.
The instruction referenced (i.e. the first instruction to be executed after the
RESET signal is applied) will be found by combining the Instruction Pointer
(offset address) with the Code Segment Register (paragraph address). The loca-
tion of the instruction referenced is FFFF0 (i.e. F0000
+
FFF0). Note that the
PC's ROM physically occupies addresses F0000 to FFFFF and that, following