Hardware Reference
In-Depth Information
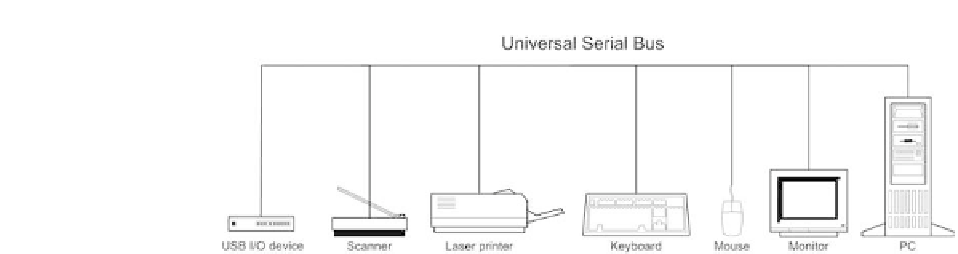
Figure 2.8
USB arrangement for connecting a wide variety of peripheral
devices
Photo 2.14
Some typical USB devices; a 256 MB memory stick, a Flash
memory card reader, and a wireless network adapter
Figure 2.8 shows a typical range of peripherals that can be connected to a PC by
means of the Universal Serial Bus. USB connectivity on a device can be easily
recognized by the presence of the USB icon (see Figure 2.9).
The main features (and notable advantages compared with serial-port data
transfer) of USB are as follows:
•
Easy to set up and configure
•
Simple cabling and connecting system
•
Devices can be identified and configured automatically
•
Peripheral devices can be 'hot-plugged' and 'hot un-plugged'
•
Suitable for a wide range of device bandwidths
•
Supports various types of data transfer (including isochronous)
•
Supports concurrent operation of a large number of up to 127 devices
•
Supports transfer of multiple data and message streams between the host and
devices
•
Efficient and transparent bus protocol
•
Conforms with standard plug-and-play architecture
•
Wide bandwidth
•
Ability to use entire bus bandwidth in isochronous mode
•
Flexible (easy to extend and modify)
Figure 2.9
The USB icon