Image Processing Reference
In-Depth Information
Fig. 2.2.
Digitization of signals and images.
2.2.3 Three-dimensional images
In this section, we will address 3D images.
A
3D continuous image
is defined by a scalar (real) function of three
variables
f
(
x, y, z
), where
f
represents a characteristic value at a point (
x, y, z
)
in 3D space.
A 3D continuous image is digitized in the same way as the 2D case; that
is, a function
f
is sampled at points of a cubic ordered array (3D grid or
3D lattice of sample points). Otherwise, the 3D space is divided into a set of
small cubic cells, and the value of the function
f
averaged over each cube is
assigned it . Hence, the cube is called
volume cell
or
voxel
instead of a pixel in
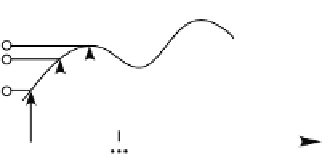


























Search WWH ::

Custom Search