Image Processing Reference
In-Depth Information
8
8
8
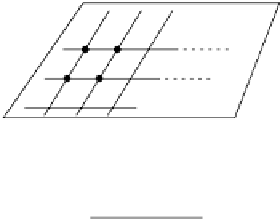
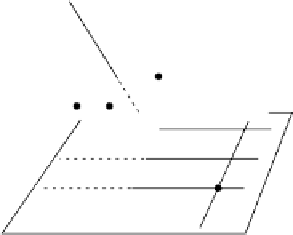
Fig. 7.4.
Illustration of projection. A density value
g
P
of a point P = (
u, v
)on2D
projection plane
P
l
is obtained by adding density of values of voxels (
i, j, k
)in3D
space in the direction of a projection line
l
P
.
7.3.3 Projection
As was stated in Section 2.2.5,
projection
means the integration of a 3D image
along a line
l
p
perpendicular to a plane
P
L
. In this chapter we extend the
integration a little so that it includes a kind of mapping of a density value.
Here a mapped value is calculated by various ways from the density values of
a 3D image on the line
l
p
and is given to an intersection of the line
l
p
and the
plane
P
L
. A result of projection is a 2D image and is presented on a display.
There are several ways to calculate a mapped value. The following two types
have been widely used in medical image processing (Fig. 7.4).
Denoting by
g
P
a density value of a point P on a plane
P
l
,
g
P
=
(i)
w
(
x, y, z
)
f
(
x, y, z
)
ds
(7.2)
l
P
where
l
P
is the integration along the normal
l
P
of a projection plane
P
l
,
and
w
(
x, y, z
) is a suitable weight function.
(ii)
g
P
=max
l
P
{
w
(
x, y, z
)
f
(
x, y, z
)
}
(7.3)
where max
l
P
is the maximum density on the above line
l
P
and
w
(
x, y, z
)is
a suitable weight function.









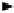

Search WWH ::

Custom Search