Image Processing Reference
In-Depth Information
(
a
)
(
b
)
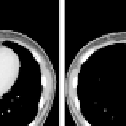
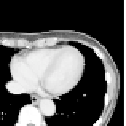
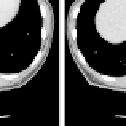
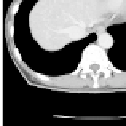
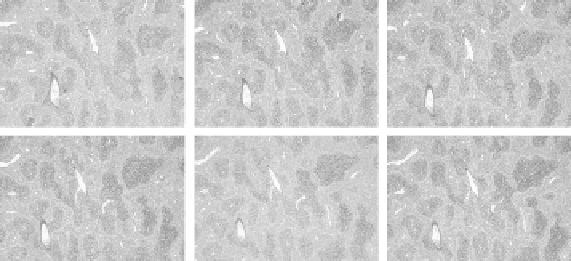
Fig. 1.2.
Examples of 3D images: (
a
) Slices of CT images of the human body; (
b
)
microscope images of tissue sections.
the closest to true 3D. Recent devices are approaching true 3D images with an
approximately isotropic resolution of 1 mm [Bankman00, Ritman03]. These
images require large amounts of data, and in a medical setting there is a good
chance that many images, for example, 512
×
512
×
512 3D gray-scale images,
might be created.
The principles behind CT also are being applied to other fields. One well-
known example is emission CT, where radioactive isotopes (RIs) are injected
into patients, and then gamma ray emissions are acquired to recreate cross
sections (see Remark 1.4). X-ray CT has also started to be used for the internal
inspection and measurement of industrial products. New applications are also
attracting attention, including, for example, applications to computer-aided
design (CAD), precise measurement of products, and internal inspection of
machine parts while the device is in operation [Hardin00]. In each case, the









Search WWH ::

Custom Search