Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
for net work management. It polls agents on the net work and cor relate s and dis plays the
management information.
MIB
A Management Information Base (MIB) is a collection of information that is stored on the
local agent of the managed device. MIBs are organized hierarchically and are accessed by
the NMS. MIBs are databases of objects organized in a tree-like structure, with each
branch containing similar objects. Each object has a unique object identifier (number) that
uniquely identifies the managed object of the MIB hierarchy. Read and write community
strings are used to control access to MIB information.
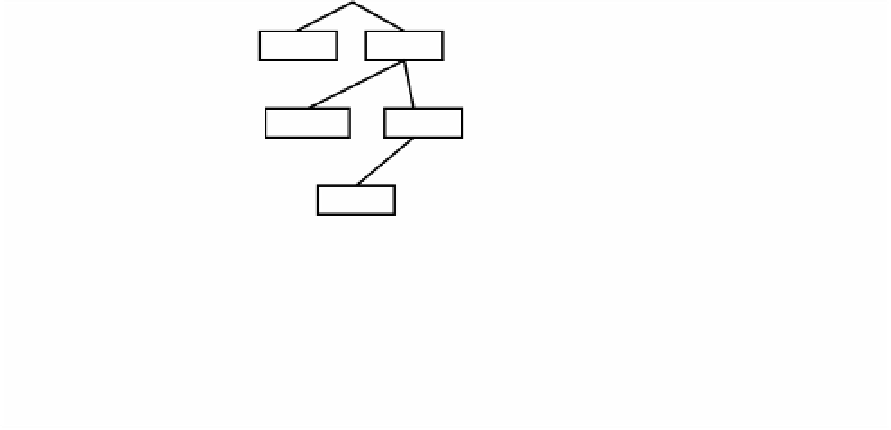
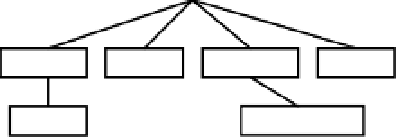
The top-level MIB object IDs belong to different standards organizations, and lower-level
object IDs are allocated to associated organizations. Standard MIBs are defined by RFCs.
Ve n d o r s d e f i n e p r i v a t e b r a n c h e s t h a t i n c l u d e m a n a g e d o b j e c t s fo r t h e i r p r o d u c t s . F i g u r e
15-2 shows a portion of the MIB tree structure. RFC 1213 describes the MIBs for TCP/IP.
Cisco defines the MIBs under the Cisco head object. For example, a Cisco MIB can be
uniquely identified by either the object name, iso.org.dod.private.enterprise.cisco, or the
equivalent object descriptor, 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.
ccitt (0)
iso (1)
mem (2)
org (3)
dod (6)
internet (1)
mgmt (2)
exp (3)
private (4)
sec (5)
mib (1)
enterprise (1)
system (1)
IP (4)
TCP (6)
UDP (7)
SNMP (11)
cisco (9)
Figure 15-2
MIB Tree Structure
Each individual manageable feature in the MIB is called a MIB variable. The MIB module
is a document that describes each manageable feature that is contained in an agent. The
MIB module is written in Abstract Syntax Notation 1 (ASN.1). Three ASN.1 data types are
required: name, syntax, and encoding. The name serves as the object identifier. The syntax
defines the object's data type (integer or string). The encoding data describes how infor-
mation associated with a managed object is formatted as a series of data items for trans-
mission on the network. Some examples of standard managed objects that can be
obtained from the MIB tree are as follows:
Interfaces
■
Buffers
■