Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
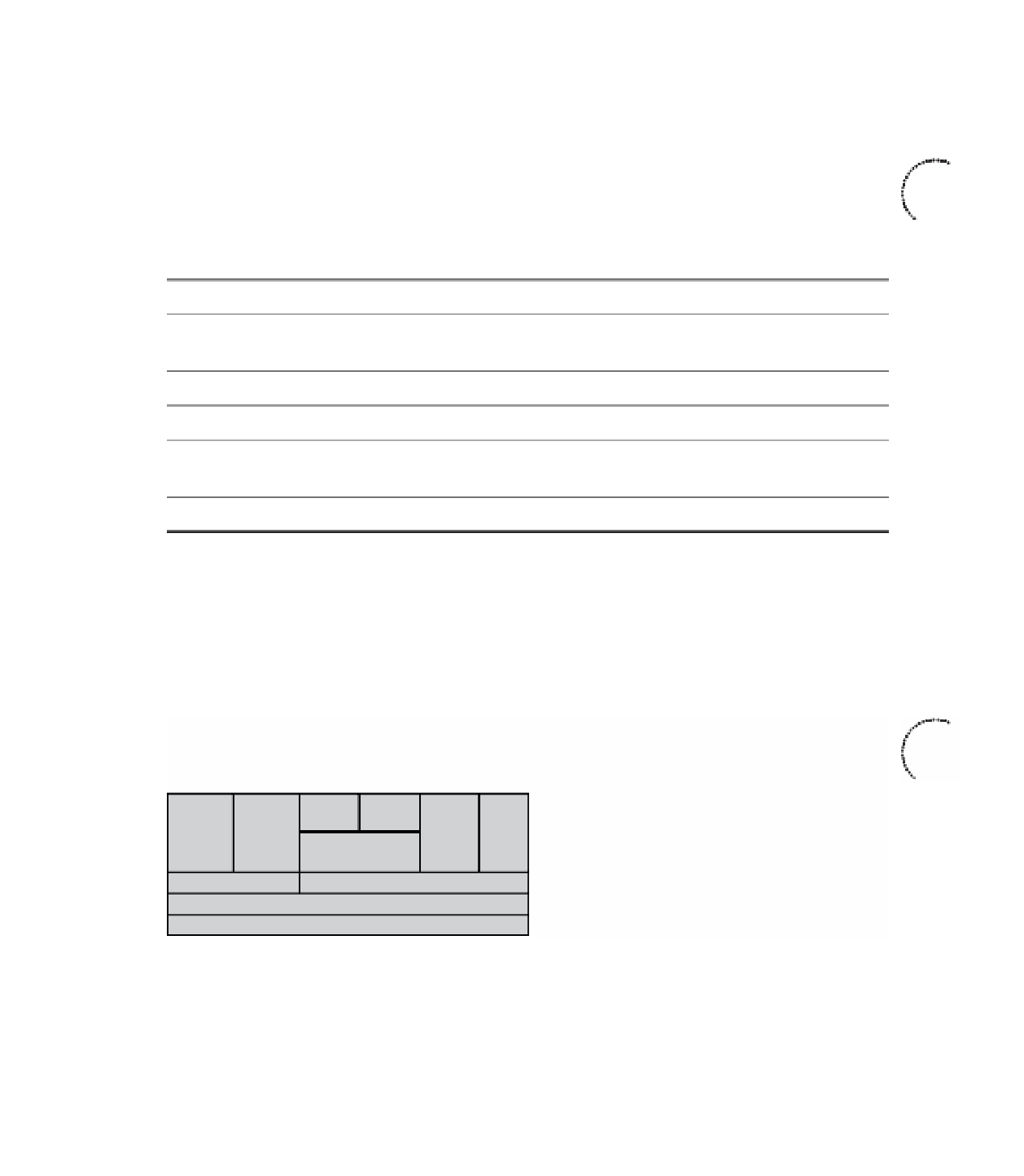
each codec. For example, the established MOS score for G.711 is 4.1, and G.729 is 3.92.
The default codec setting for VoIP dial peers in Cisco IOS software is G.729 (g729r8), but
this can be configured with several other options, including G.711. Other codec standards
are shown in Table 14-8. An explanation of the compression techniques is beyond the
scope of the CCDA test.
Ta b l e 1 4 - 8
Codec Standards
Key
To p i c
Codec
Bit Rate
MOS
Description
G.711u
64 kbps
4.1
PCM. Mu-law version used in North America and Japan. Sam-
ples speech 8000 times per second, represented in 8 bits.
G.711a
64 kbps
4.1
PCM. A-law used in Europe and international systems.
G.726
16/24/32/40
kbps
3.85
Adaptive differential pulse-code modulation (AD-PCM).
G.728
16 kbps
3.61
Low-Delay CELP (LDCELP).
G.729
8 kbps
3.92
Conjugate Structure Acelp (Cs-Acelp).
G.723.1
6.3 kbps
3.9
Multipulse Excitation-Maximum Likelihood Quantization
(MPE-MLQ).
G.723.1
5.3 kbps
3.65
Algebraic Code-Excited Linear Prediction (ACELP).
VoIP Control and Transport Protocols
A number of different protocols are used in a VoIP environment for call control, device
provisioning, and addressing.
Figure 14-15 shows those protocols focused on VoIP control and transport.
Audio
and
Video
Control Control
RAS
Key
To p i c
Call Control
Audio
Video
G.7xx
H.26x
RTCP
H.225
Q.931
H.245
RTP
TCP
UDP
IP
Layer 2: FR, MPLS, Ethernet, PPP
Figure 14-15
Vo I P C o n t r o l a n d Tr a n s p o r t P r o t o c o l s