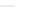Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
Operations &
Serviceability
User and Device
Provisioning
Voice Quality
Monitoring & Alerting
Operations & Fault
Monitoring
Network & Application
Probing
WWW
HDTV
Applications
& Services
C
CC
Voice
Messaging
Presence
Services
Rich Media
Conferencing
Collaboration
Clients
Mobility
Contact Center
ICM
Call
Control
V
M
MP
CIP
CIP
LDAP &
Directory Services
Media
Resources
MoH
End Points
Unified CUCM
Applications
Device
Mobility
Call
Routing
V
Dial Plan & Call
Admission Control
Video
Telephony
PSTN
Services
Call
Processing
PSTN & IP
Gateways
Remote Site
Survivability
IP
Network
Wireless
Access
Switch
Firewall
Security
Quality of
Service
IP WAN &
Internet Access
Distribution &
Core Switching
WAN
Router
Figure 14-6
Cisco Unified Network
In multiservice networks, digitized (coded) voice is packaged into packets, cells, or
frames; sent as data throughout the networks; and converted back to analog voice. The un-
derlying protocols used for these converged services are
Vo i c e o v e r F r a m e Re l a y ( Vo F R )
■
Vo i c e o v e r A s y n c h r o n o u s Tr a n s fe r M o d e ( Vo AT M )
■
Vo i c e o v e r I n t e r n e t P r o t o c o l ( Vo I P )
■
Initially, VoFR and VoATM were used but lost ground to VoIP solutions. VoFR and
Vo AT M a r e n o l o n g e r e x a m t o p i c s fo r t h e C C DA a n d a r e n o t c o v e r e d f u r t h e r. Vo I P i s a l s o
referred to as IP telephony (IPT) when it is integrated with IP-based signaling and call con-
trol. Most new phone system deployments are IPT systems.
VoIP
Vo I P provides transport of voice over the IP protocol family. IP makes voice globally
available regardless of the data-link protocol in use (Ethernet, AT M , Frame Relay). With
Vo I P, enterprises do not have to build separate voice and data networks. Integrating voice
and data into a single converged network eliminates duplicate infrastructure, management,
and costs.