Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
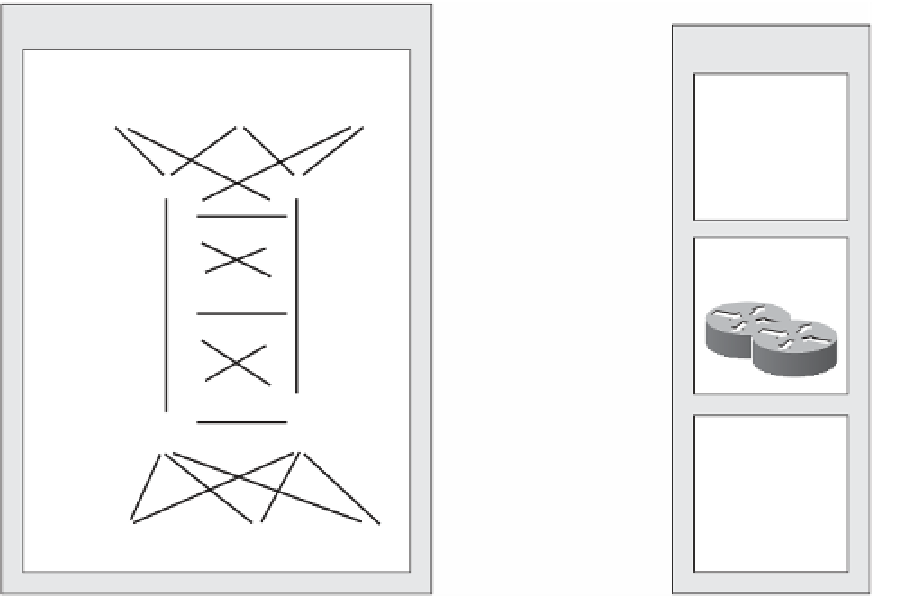
Enterprise Campus
EIGRP
OSPF
BGP
Static
Enterprise Edge
Data Center
E-Commerce/
DMZ/Internet
Enterprise
WAN
Campus
Core
EIGRP
OSPF
Building
Distribution
BGP
Static
Remote
Access VPN,
Internet
Building
Access
Figure 11-23
Routing Protocols on the Hierarchical Network Infrastructure
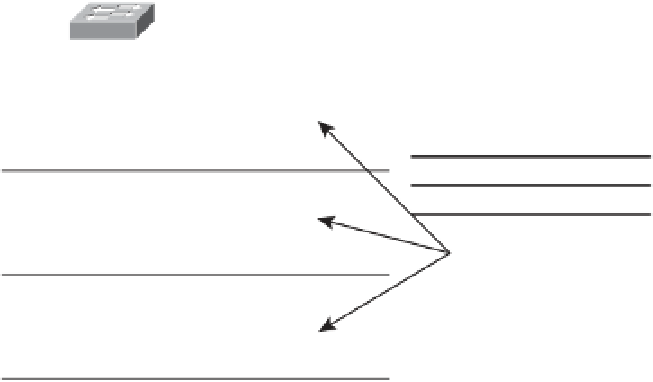
With multicast, packets are sent to a multicast group, which is identified with an IP multi-
cast address. Multicast supports the transmission of IP packets from one source to multi-
ple hosts. Packets with unicast addresses are sent to one device, and broadcast addresses
are sent to all hosts; packets with multicast addresses are sent to a group of hosts.
Multicast Addresses
Multicast addressing uses Class D addresses from the IPv4 protocol. Class D addresses
range from 224.0.0.0 to 239.255.255.255. IANA manages multicast addresses.
Routing protocols (RIPv2, EIGRP, and OSPF) use multicast addresses to speak to their
neighbors. For example, OSPF routers use 224.0.0.6 to speak to the designated router (DR)
in a multiaccess network. Class D multicast addresses range from 224.0.0.0 to
239.255.255.255. Multicast addresses in the range of 224.0.0.1 to 224.255.255.255 are re-
served for special addresses or network protocol on a multiaccess link. RFC 2365 reserves
multicast addresses in the range of 239.192.000.000 to 239.251.255.255 for organization-
local scope. Similarly, 239.252.000.000 to 239.252.255.255, 239.254.000.000 to
239.254.255.255, and 239.255.000.000 to 239.255.255.255 are reserved for site-local scope.
Key
To p i c
Ta ble 1 1-1 0 lists some well-known and multicast address blocks.