Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
LWA P P
Lightweight Access Point Protocol (LWAPP) is a draft Internet Engineering Task Force
(IETF) standard for control messaging for setup, authentication, and operations between
APs and WLAN controllers (WLC).
In the LWAPP RFC draft, LWAPP control messages can be transported at Layer 2 tunnels
or Layer 3 tunnels. Layer 2 LWAPP tunnels were the first method developed in which the
APs did not require an IP address. The disadvantage of Layer 2 LWAPP was that the WLC
needed to be on every subnet on which the AP resides. Layer 2 LWAPP is a deprecated so-
lution for Cisco. Layer 3 LWAPP is the preferred solution. In the configuration, Layer 2 or
Layer 3 transport modes can be selected. When set Layer 3, the LWAPP uses IP addresses
to communicate with the access points; these IP addresses are collected from a mandatory
DHCP server. When set to Layer 2, the LWAPP uses proprietary code to communicate
with the access points.
Note:
Layer 2 LWAPP tunnels use EtherType code 0xBBBB. Layer 3 LWAPP uses UDP
ports 12222 and 12223.
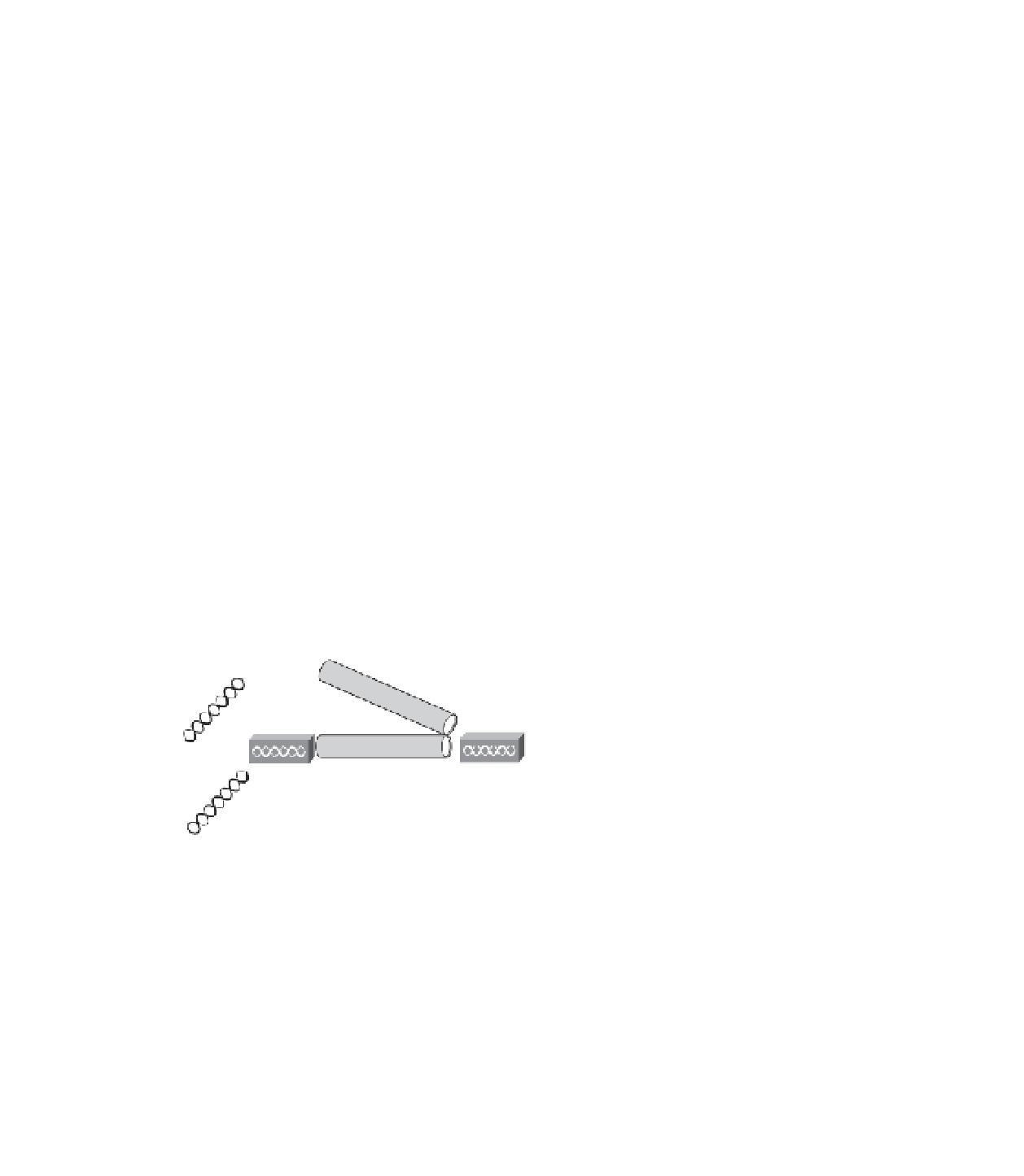
As shown in Figure 5-3, Layer 3 LWAPP tunnels are used between the LWAP and the
WLC. Messages from the WLC use User Datagram Port (UDP) port 12223 for control
and UDP port 12222 for data messages. In this solution, APs require an IP address, but the
WLC does not need to reside on the same segment.
Wired
Network
LWAP
LWAP
L3 LWAPP Tunnels
WLC
Wireless Clients
Figure 5-3
Layer 3 LWAPP