Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
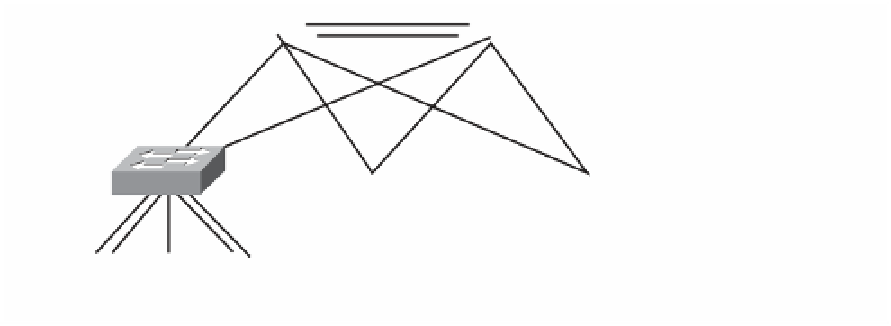
Core Switches
Si
Si
Server Farm
Switches
Figure 3-14
Server Farm
Server Connectivity Options
Servers can be connected in three primary ways:
Single network interface card (NIC)
■
Dual NIC EtherChannel
■
Dual NIC to separate access switches
■
Content switching
■
Single NIC connected servers contain Fast or Gigabit Ethernet full-duplex speeds with no
redundancy. Servers requiring redundancy can be connected with dual NICs using switch
EtherChannel or each link connected to separate access switches.
Advanced redundancy solutions use content switches that front end multiple servers. This
provides redundancy and load balancing per user request.
Enterprise Data Center Infrastructure
Data centers (DC) contain different types of server technologies, including standalone
servers, blade servers, mainframes, clustered servers, and virtual servers.
Figure 3-15 shows the enterprise DC. The DC access layer must provide the port density
to support the servers, provide high-performance/low-latency Layer 2 switching, and
support dual and single connected servers. The preferred design is to contain Layer 2 to
the access layer and Layer 3 on the distribution. Some solutions push Layer 3 links to the
access layer. Blade chassis with integrated switches and virtual machines have become a
popular solution for DCs. Cisco Data Center 3.0 architecture is the next evolution of the
DC. DC architecture is covered in detail in Chapter 4, “Data Center Design.”
The DC aggregation layer (distribution layer) aggregates traffic to the core. Deployed on
the aggregation layer are
Load balancers
to provide load balancing to multiple servers
■
SSL offloading devices
to terminate Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) sessions
■