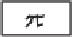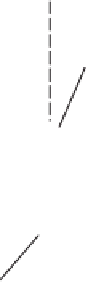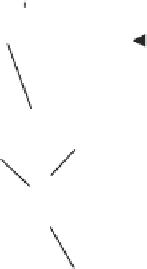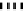Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
performs controlled swapping of two input bits
x
1
and
x
2
. The output bits are
y
1
=
x
2
and
y
2
0. Let IN with
n
-bit input and
n
-bit output be controlled with
m
-bit vector
V
. Then we shall denote such IN as
P
n
;
m
.
The general structure of the layered box
P
n
;
m
is presented in Fig. 1, where fixed per-
mutations represent fixed connections and each active layer
L
represents
n
=
x
1
,if
v
=
1, or
y
1
=
x
1
and
y
2
=
x
2
,if
v
=
2 parallel
elementary boxes
P
2;1
, i. e. some single-layer CP box. In present paper dotted lines cor-
responding to CP boxes indicate the controlling bits. The box
P
n
;
m
can be represented
as a superposition of the operations performed on bit sets:
/
P
(
V
)
L
(
V
1
)
◦
π
L
(
V
2
)
◦
π
L
(
V
s
)
,
=
◦
◦ ... ◦
π
◦
n
;
m
1
2
s
−
1
where
π
k
are fixed permutations (
k
=
1
,
2
,...,
s
−
1) ,
V
j
is the component of
V
,which
controls the
j
th active layer (
j
n
), and
s
is the
number of active layers
L
(
V
j
)
. Design of the CP boxes with required properties consists
in selecting respective fixed permutations. One can easy construct the layered box
P
−
1
n
;
m
=
1
,
2
,...,
s
;
V
=(
V
1
,
V
2
,...,
V
s
)
;
s
=
2
m
/
which is inverse of
P
n
;
m
-box:
P
−
1
n
;
m
(
V
)
L
(
V
s
)
◦
π
−
1
s
L
(
V
s
−
1
)
◦
π
−
1
s
◦ ... ◦
π
−
1
1
L
(
V
1
)
.
=
◦
◦
−
1
−
2
In accordance with the structure of the CP boxes
P
n
;
m
and
P
−
1
n
;
m
we shall assume that in
CP boxes denoted as
P
n
;
m
the switching elements
P
2;1
are consecutively numbered from
left to right and
from top to bottom
. In CP boxes denoted as
P
−
1
n
;
m
the elementary boxes
P
2;1
are numbered from left to right and
from bottom to top.
Thus, for all
i
}
the
i
th bit of the controlling vector
V
controls the
i
th box
P
2;1
in both boxes
P
n
;
m
and
P
−
1
∈{
1
,
2
,...,
m
n
;
m
.For
j
=
1
,
2
,...,
s
the component
V
j
of the vector
V
controls the
j
-th active layer in
-th layer in
P
−
1
the box
P
n
;
m
and the
(
s
−
j
+
1
)
n
;
m
.
x
3
x
4
x
n
-1
x
n
a)
x
1
x
2
X
b)
Y
c)
n
n
v
1
v
n
/
2
v
2
V
s
V
1
P
2
;
1
P
2;1
P
2;1
L
L
Fixed permutation
-1
s
-1
1
1
v
n
/2
+2
v
n
v
n
/2
+1
V
s
-1
V
2
P
2
;
1
P
2;1
P
2
;
1
L
L
-1
Fixed
per
m
utation
s-
1
s
-1
v
m-n
/2+1
v
m-n
/2+2
v
m
V
s
V
1
P
2;1
P
2;1
P
2;1
L
L
n
n
y
1
y
2
y
3
y
4
y
n
-1
y
n
Y
X
Fig. 1.
General structure of the boxes
P
n
;
m
(a,b) and
P
−
1
n
;
m
(c)