Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
T
: The validity period of signer's certificate
(
T
=
t
2
− t
1
, where
t
1
is the issuance time and
t
2
is the expiration time)
t
: Acceptors' average recency period
(
T
=
n × t
, where we assume that
n
is an integer)
q
: The average number of transactions between the signer and the ac-
ceptors during the recency period
t
, the validity
period of signer's certificate. In OCSP, the CA has to be involved in every trans-
action and generate an OCSP response for each
The signer has
nq
transactions with the acceptors, during
T
nq
transaction. However, ACSP
responses are generated only
times in average, because signer's certificate is
replaced by a new certificate in every recency period
n
t
and this new certificate
satisfies acceptors' recency periods during
in average. To generate OCSP or
ACSP response, the CA needs the computational load of one signature genera-
tion. Hence, the number of signature generation performed by the CA is
t
nq
in
OCSP, and
in ACSP.
When an acceptor receives a message from a signer, the acceptor has to decide
whether signer's certificate is valid or not. For this decision, the acceptor may
need more communications with the CA and the signer. We will consider this
communicational overhead. In OCSP, the acceptor has to send an OCSP request
and the CA has to send an OCSP response for each
nq
transaction. Therefore,
the communicational overhead of OCSP is 2
n
. In ACSP, the acceptor does not
need additional communications if signer's certificate satisfies acceptor's recency
period. If signer's certificate does not satisfy acceptor's recency period, three
more passes are needed. Hence, the communicational overhead of ACSP is 3
nq
n
in
average.
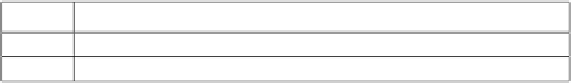
Tabl. 2 summarizes the above analysis. As you can see, ACSP reduced CA's
signature generation by 1
/q
. The computational cost of ACSP is much cheaper
than that of OCSP.
Table 2.
The comparison of eciency in OCSP and ACSP
CA's signature generation
Communicational overhead
OCSP
nq
2
nq
ACSP
n
3
n
additional communication
passes, while ACSP needs 3
n
additional communication passes. Therefore, if
q
is
greater than 1.5, i.e. if there are more than or equal to two transactions during
t
In communicational overhead, OCSP requires 2
nq
, ACSP requires smaller communicational overhead than OCSP.
For very small
, the size of total packets in ACSP can be larger than that
in OCSP, because the size of an ACSP response is larger than that of an OCSP
response. This can be the only drawback of ACSP, but the size of total packets
in ACSP becomes smaller than that in OCSP as the value of
q
q
grows.