Geology Reference
In-Depth Information
?
is almost entirely basaltic and intrudes into vertical frac-
tures to form dikes and pillow lava fl ows (see Figure 5.7).
As successive injections of magma cool and solidify, they
form new oceanic crust and record the intensity and ori-
entation of Earth's magnetic field (Figure 2.12). Diver-
gent boundaries most commonly occur along the crests of
oceanic ridges—for example, the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. Oce-
anic ridges are thus characterized by rugged topography
with high relief resulting from displacement of rocks along
large fractures, shallow-depth earthquakes, high heat fl ow,
and basaltic fl ows or pillow lavas.
Divergent boundaries are also present under continents
during the early stages of continental breakup. When magma
wells up beneath a continent, the crust is initially elevated,
stretched, and thinned, producing fractures, faults, rift val-
leys, and volcanic activity
(
What Would You Do
You've been selected to be part of the fi rst astronaut team to
go to Mars. While your two fellow crew members descend to
the Martian surface, you'll be staying in the command module
and circling the Red Planet. As part of the geologic investiga-
tion of Mars, one of the crew members will be mapping the
geology around the landing site and deciphering the geologic
history of the area. Your job will be to observe and photo-
graph the planet's surface and try to determine whether Mars
had an active plate tectonic regime in the past and whether
there is current plate movement. What features would you
look for, and what evidence might reveal current or previous
plate activity?
◗
Figure 2.16a). As magma
intrudes into faults and frac-
tures, it solidifi es or fl ows out
onto the surface as lava fl ows;
the latter often covering the
rift valley fl oor (Figure 2.16b).
The East African Rift Valley is
an excellent example of con-
tinental breakup at this stage
(
Figure 2.17a).
As spreading proceeds,
some rift valleys continue to
lengthen and deepen until the
continental crust eventually
breaks and a narrow linear sea
is formed, separating two con-
tinental blocks (Figure 2.16c).
The Red Sea separating the
Arabian Peninsula from Africa
(Figure 2.17b) and the Gulf
of California, which separates
Baja California from mainland
Mexico, are good examples of
this more advanced stage of
rifting.
As a newly created nar-
row sea continues to enlarge,
it may eventually become an
expansive ocean basin such
as the Atlantic Ocean basin is today, separating North and
South America from Europe and Africa by thousands of
kilometers (Figure 2.16d). The Mid-Atlantic Ridge is the
boundary between these diverging plates (Figure 2.11); the
American plates are moving westward, and the Eurasian
and African plates are moving eastward.
◗
◗
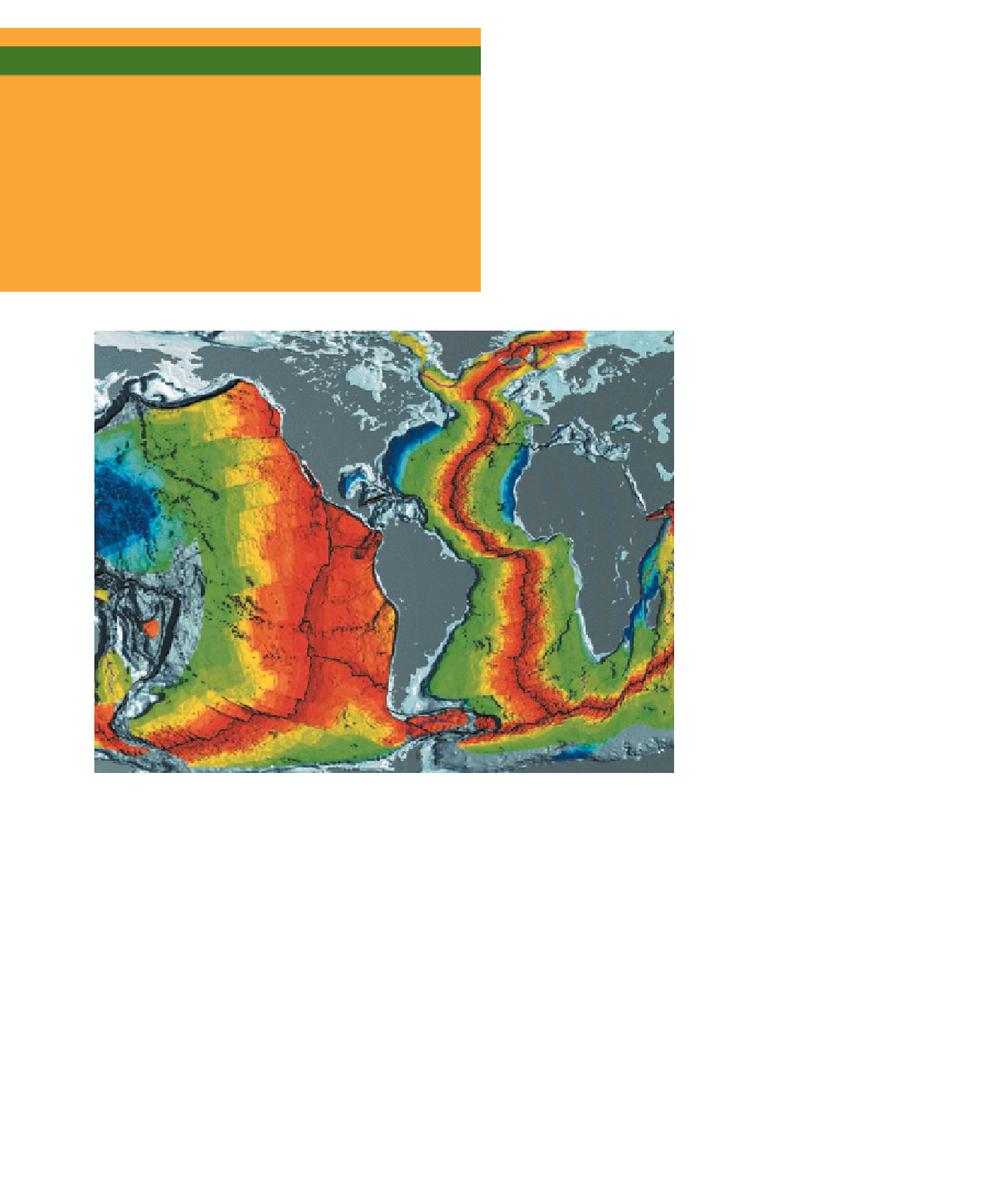
Figure 2.13
Age of the World's Ocean Basins The age of the world's ocean basins has been
determined from magnetic anomalies preserved in oceanic crust. The red colors adjacent to the
oceanic ridges are the youngest oceanic crust. Moving laterally away from the ridges, the red colors
grade to yellow at 48 million years ago, to green at 68 million years ago, and to dark blue some
155 million years ago. The darkest blue color is adjacent to the continental margins and is just
somewhat less than 180 million years old.
slide laterally past one another. Interaction of plates at their
boundaries accounts for most of Earth's volcanic eruptions
and earthquakes, as well as the formation and evolution of
its mountain systems.
Divergent plate boundaries
or
spreading ridges
occur where
plates are separating and new oceanic lithosphere is form-
ing. Divergent boundaries are places where the crust is ex-
tended, thinned, and fractured as magma, derived from the
partial melting of the mantle, rises to the surface. The magma
An Example of Ancient Rifting
What features in the geo-
logic record can geologists use to recognize ancient rifting?
Associated with regions of continental rifting are faults, dikes
(vertical intrusive igneous bodies), sills (horizontal intrusive
Search WWH ::

Custom Search