Geology Reference
In-Depth Information
180
°
140
°
100
°
60
°
20
°
20
°
60
°
100
°
140
°
180
°
Arctic Ocean
60
°
60
°
Canadian
shield
40
°
40
°
Atlantic
Ocean
Pacific
Ocean
20
°
20
°
0
°
0
°
Indian
Ocean
20
°
20
°
◗
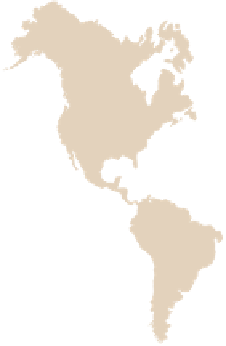
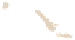
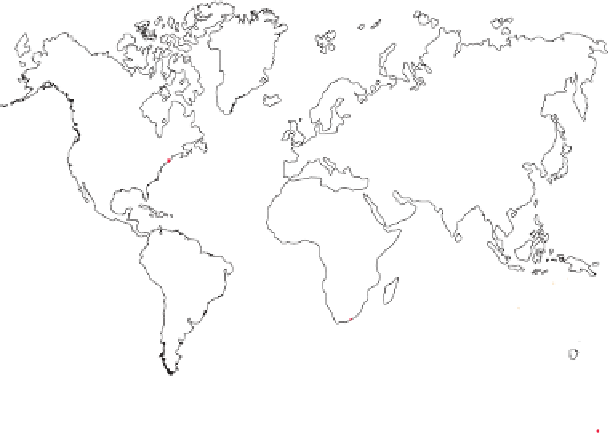
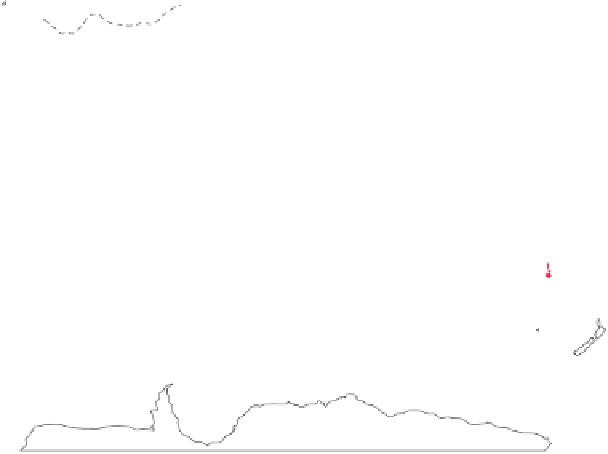
Figure 19.5
The Distribution
of Precambrian Rocks Areas
of exposed Precambrian rocks
constitute the shields, whereas
the platforms consist of buried
Precambrian rocks. A shield and its
adjoining platform make up a craton.
40
°
Exposed Precambrian rocks
Covered Precambrian rocks
40
°
60
°
60
°
180
°
140
°
100
°
60
°
20
°
20
°
60
°
100
°
140
°
180
°
◗
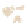
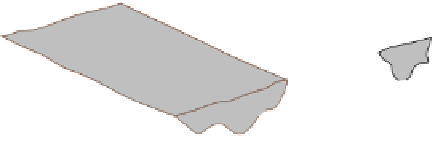
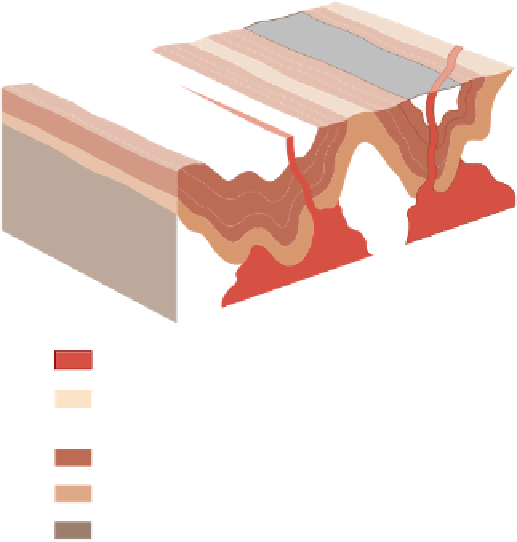
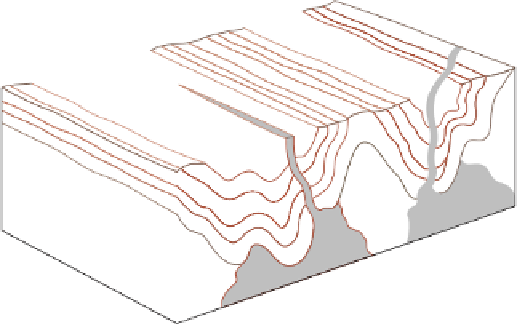
Figure 19.6
Greenstone Belts and Granite-Gneiss Complexes
b
Pillow lava of the Ispheming greenstone belt in Michigan.
Granitic intrusives
Upper sedimentary unit: sandstones and shales
most common
Middle volcanic unit: mainly basalt
Lower volcanic unit: mainly peridotite and basalt
Granite-gneiss complex
a
Two adjacent greenstone belts. Older belts—those more than 2.8
billion years old—have an ultramafi c unit overlain by a basaltic unit.
In younger belts, the succession is from a basaltic unit. In younger
belts, the succession is from a basaltic lower unit to an andesite-
rhyolite unit.
c
Gneiss from a granite-gneiss complex in Ontario, Canada.




















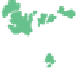






































































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search