Geology Reference
In-Depth Information
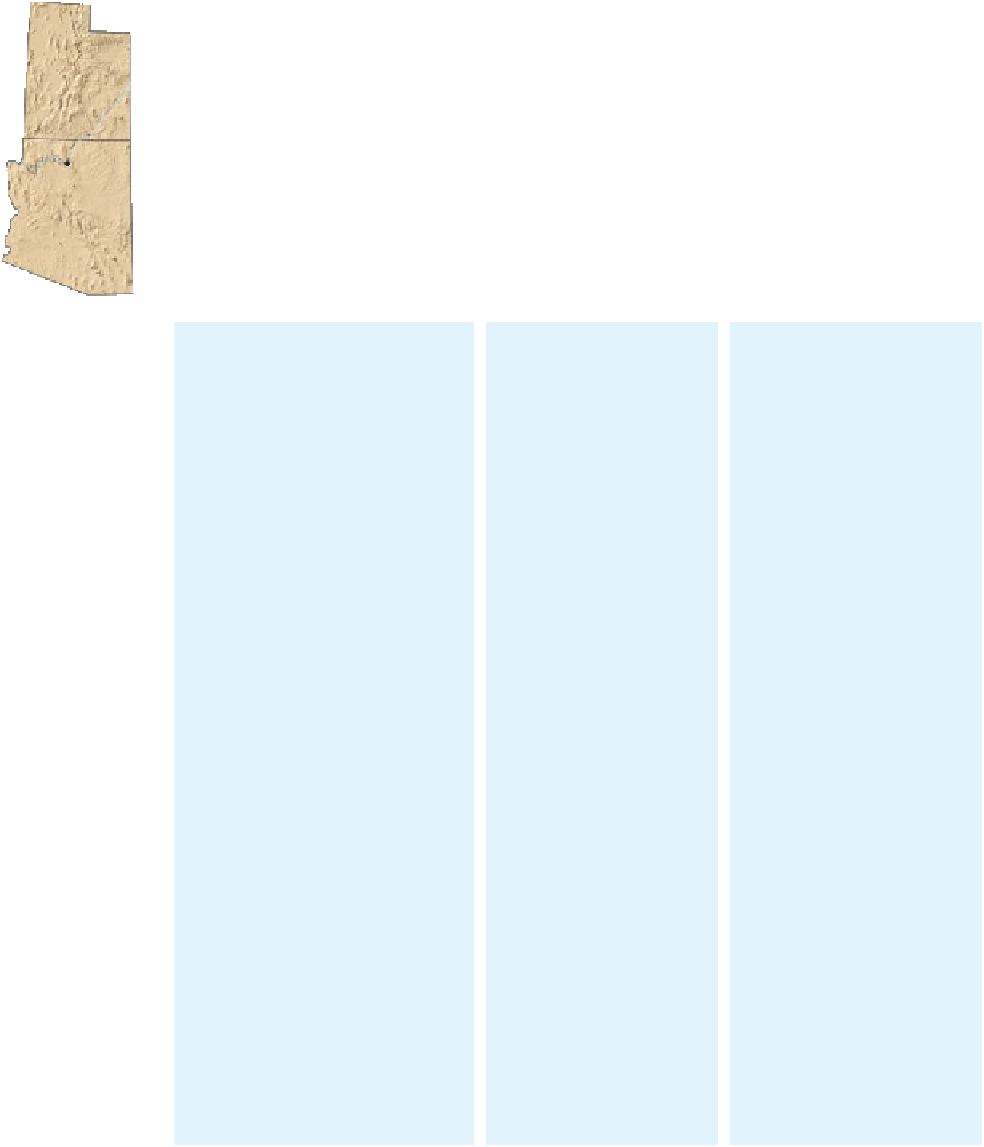
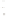
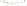
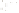
UTAH
Bryce
Canyon
Zion
Grand
Canyon
ARIZONA
Grand Canyon
National Park
Arizona
Zion
National Park
Utah
Bryce Canyon
National Park
Utah
Paleogene Period
Wasatch Fm
Kaiparowits Fm
Wahweap Ss
Cretaceous Period
Straight Cliffs Ss
Tropic Shale
Dakota Ss
Winsor Fm
Curtis Fm
Jurassic Period
Entrada Ss
Carmel Fm
Carmel Fm
Navajo Ss
Navajo Ss
Kayenta Fm
Older rocks not exposed
Wingate Ss
Triassic Period
Chinle Fm
Moenkopi Fm
Moenkopi Fm
Kaibab Ls
Toroweap Fm
Kaibab Ls
Permian Period
Coconino Ss
Hermit Shale
Older rocks not exposed
Supai Fm
Pennsylvanian Period
Mississippian Period
Redwall Ls
Temple Butte Ls
Devonian Period*
Mauv Fm
Bright Angel Shale
Cambrian Period
Colorado
River
Tapeats Ss
Vishnu Schist
Precambrian
Fm = Formation
Ss = Sandstone
Ls = Limestone
*
Rocks of Ordovician and Silurian age are not present in the Grand Canyon.
◗
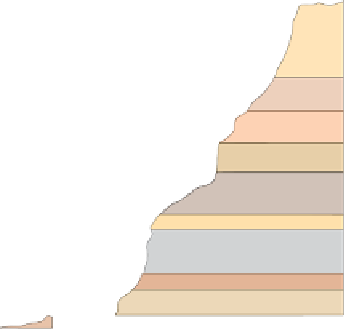
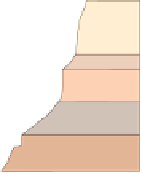
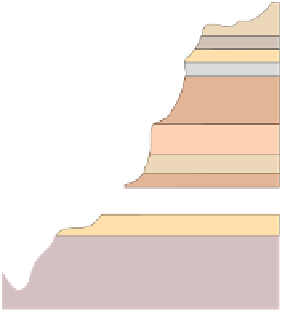
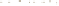
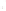
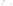
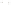
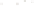
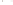
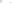
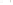
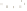
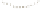
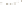
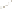
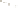
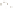
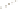
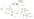
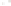
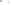
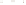
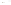
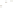
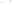
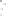
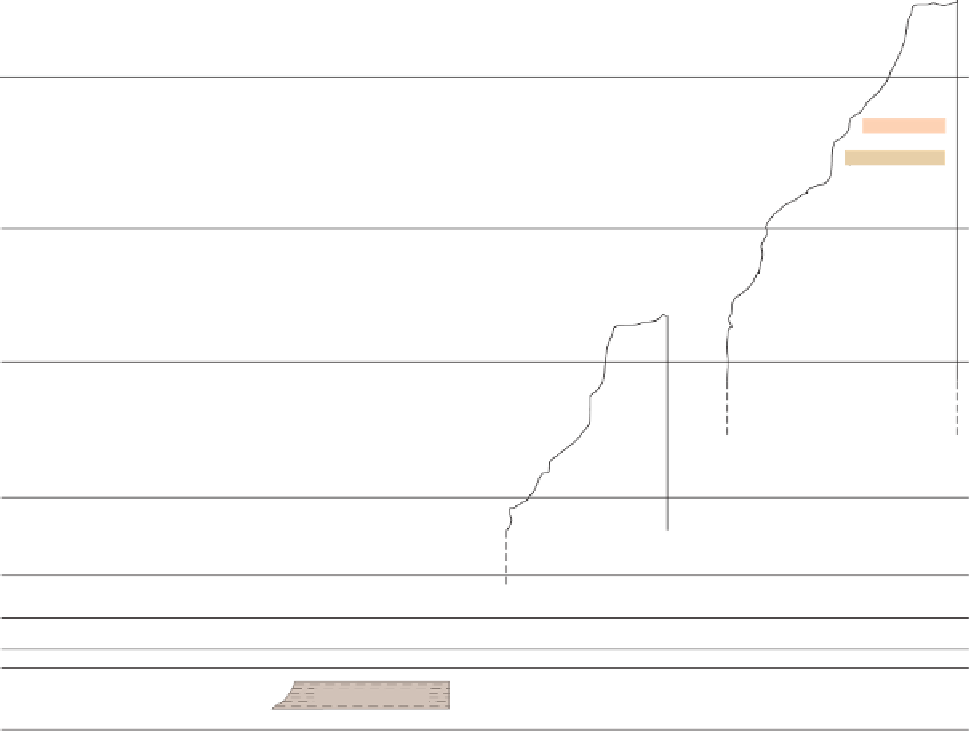
Figure 17.14
Correlation of Rock Units within the Colorado Plateau At each location, only a portion of the geologic record of the Colorado
Plateau is exposed. By correlating the youngest rocks at one exposure with the oldest rocks at another exposure, geologists can determine
the entire history of the region. For example, the rocks forming the rim of the Grand Canyon, Arizona, are the Kaibab Limestone and Moenkopi
Formation—the youngest rocks exposed in the Grand Canyon. The Kaibab Limestone and Moenkopi Formation are the oldest rocks exposed
in Zion National Park, Utah, and the youngest rocks are the Navajo Sandstone and Carmel Formation. The Navajo Sandstone and Carmel
Formation are the oldest rocks exposed in Bryce Canyon National Park, Utah. By correlating the Kaibab Limestone and Moenkopi Formation
between the Grand Canyon and Zion National Park, geologists have extended the geologic history from the Precambrian to the Jurassic.
And by correlating the Navajo Sandstone and Carmel Formation between Zion and Bryce Canyon National Parks, geologists can extend the
geologic history through the Paleogene Period. Thus, by correlating the rock exposures between these areas and applying the principle of
superposition, geologists can reconstruct the geologic history of the region.
























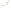
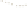





























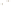

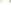


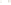
















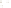



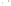






































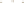




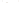









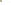
















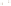
































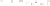
















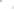



































































































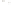



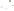


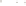

















































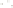

















































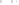














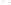
























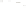



































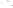



































































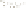









































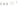







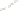






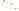











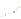


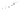




















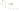


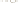





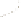




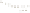















































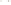





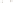

































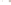
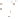






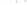






















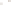
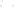




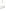

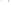

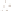



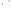



























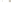

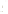

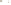































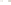







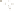

















Search WWH ::

Custom Search