Geology Reference
In-Depth Information
Weathering
Transportation
Uplift and exposure
Deposition
Sediments
Igneous rocks
(extrusive)
Lava
Lithification
(Compaction and
cementation)
Consolidation
Sedimentary
rocks
Igneous rocks
(intrusive)
Metamorphism
Metamorphic
rocks
Crystallization
Melting
Magma
◗
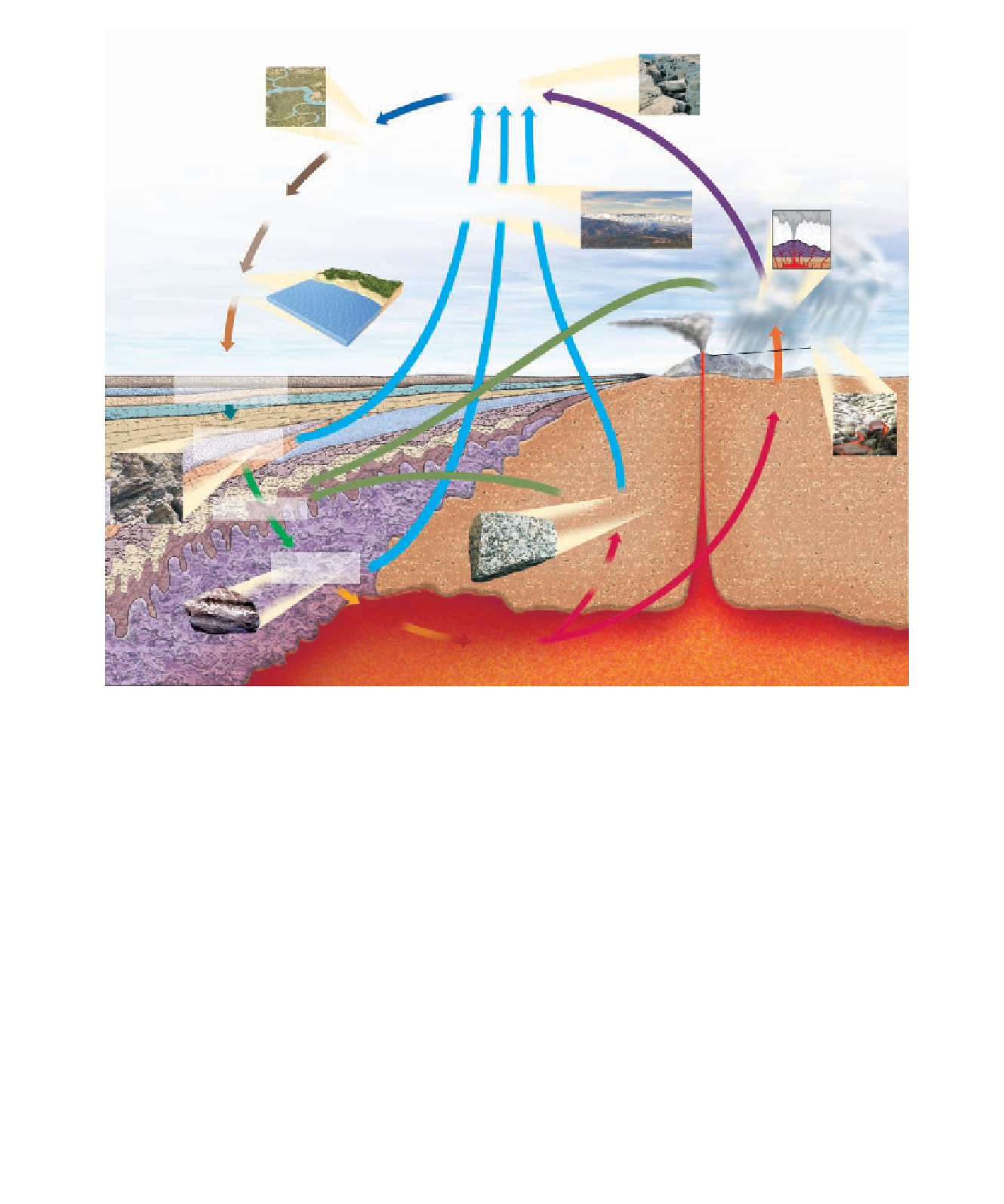
Figure 1.14
The Rock Cycle This cycle shows the interrelationships between Earth's internal
and external processes and how the three major rock groups are related. An ideal cycle includes the
events on the outer margin of the cycle, but interruptions, indicated by internal arrows, are common.
HISTORY OF LIFE
Plate tectonic theory provides us with a model for understand-
ing the internal workings of Earth and its effect on Earth's sur-
face. The theory of
organic evolution
(whose central thesis is
that all present-day organisms are related, and that they have
descended with modifi cations from organisms that lived in the
past) provides the conceptual framework for understanding
the history of life. Together, the theories of plate tectonics and
organic evolution have changed the way we view our planet,
and we should not be surprised at the intimate association be-
tween them. Although the relationship between plate tectonic
processes and the evolution of life is incredibly complex, pale-
ontological data provide indisputable evidence of the infl uence
of plate movement on the distribution of organisms.
The publication in 1859 of Darwin's
On the Origin of
Species by Means of Natural Selection
revolutionized biology
and marked the beginning of modern evolutionary biology.
With its publication, most naturalists recognized that evolu-
tion provided a unifying theory that explained an otherwise
encyclopedic collection of biologic facts.
When Darwin proposed his theory of organic evolution,
he cited a wealth of supporting evidence, including the way
organisms are classifi ed, embryology, comparative anatomy,
the geographic distribution of organisms, and, to a limited
extent, the fossil record. Furthermore, Darwin proposed that
natural selection
, which results in the survival to reproductive
age of those organisms best adapted to their environment, is
the mechanism that accounts for evolution.
Perhaps the most compelling evidence in favor of evo-
lution can be found in the fossil record. Just as the geologic
Search WWH ::

Custom Search