Geology Reference
In-Depth Information
◗
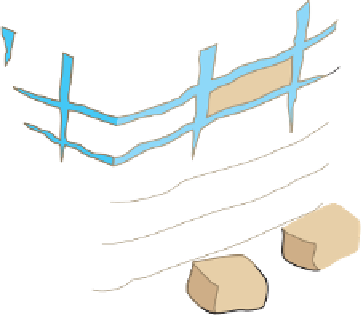
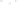
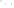
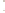
Figure 6.3 F
rost Wedging
b
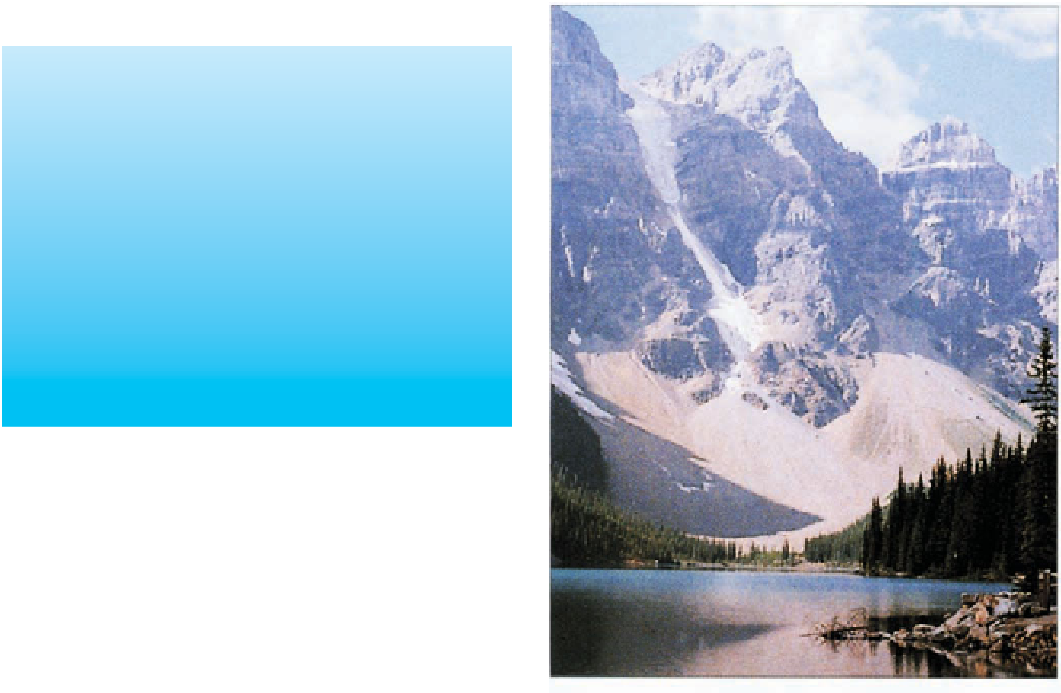
Frost wedging and other mechanical weathering processes
produced these talus accumulations in Banff National Park in the
Canadian Rocky Mountains.
a
Frost wedging takes place when water seeps into cracks and
expands as it freezes. Angular pieces of rock are pried loose by
repeated freezing and thawing.
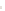
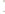
◗
Figure 6.4
Sheet Joints and Exfoliation Domes
a
Sheet joints in this body of granite in the Sierra Nevada of
California parallel the surface of the exposed rock. The rounded
mass formed by this process is an exfoliation dome.
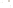
b
The sheet joint indicated by the hammer formed by expansion in
the Mount Airy Granite in North Carolina. The hammer is about
30 cm long.
composition of weathered materials. For example, several
clay minerals (sheet silicates) form by the chemical and
structural alteration of other minerals, such as potas-
sium feldspars and plagioclase feldspars, both of which
are framework silicates. Other minerals are completely
Chemical weathering
decomposes rocks and minerals by
chemical alteration of the parent material. In contrast to
mechanical weathering, chemical weathering changes the































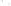







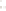











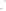





































































































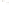

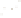

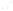





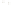























































































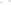






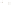
























































































































































































































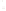






























































































































































































































































































































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search