Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
which is one is actually smaller. In such case the new value is added to the list
(Code Sample 3).
The described algorithm provides list of distances for each node. This list can be
ordered according to pairwise comparisons of fuzzy numbers in the list to produce
best possible outcome. Also all several outcomes can be presented with ranking
according to Eqs. (
2
) and (
3
).
Code Sample 3. Comparison of fuzzy distances stored in two lists
The algorithm can be implemented according to the Code Samples 1, 2, and 3.
The addition of fuzzy numbers as well as their ranking is computationally much
more complicated operation than same operations with crisp numbers. Also the
algorithm does not search only for one solution but rather for a set solutions which
is also more computationally expensive than the classic Dijkstra Algorithm. Based
on these facts it can be reasoned that the algorithm will be both computationally and
time demanding when compared to classic Dijkstra algorithm. But these are
properties of the algorithm that on the other hand allows calculation with the
uncertainty.



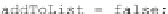





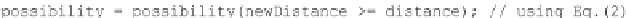








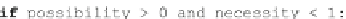
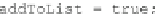

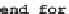






Search WWH ::

Custom Search