Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
5 Event Processing Enhancements
The main building block of web based GIS monitoring and alerting solutions is
contained inside the Weda speci
the use of duplex services. This enables
message exchange patterns in which both endpoints can send messages to the other
independently. A duplex service, therefore, can send messages back to the client
endpoint, providing event-like behaviour. Duplex communication occurs when a
client connects to a service and provides the service with a channel at which the
service can send messages back to the client. We can bene
cation
—
s Weda
endpoint which is accessible from the server. To implement the push mechanism,
the client must implement a client-speci
t from the client
'
c contract called a callback contract. As
we created our experimental system before the SES standard was proposed, our
experiments contain an easier WS-Eventing [
12
] contract (other WS-Noti
cation
[
13
] OASIS-Standard is bind able to the model). There are three types of services
needed in enhancements:
1. Subscription and noti
cation management
2. Default public integration point for sensors, monitoring systems and other event
sources
3. Integration point for admin tools for statement/topic management.
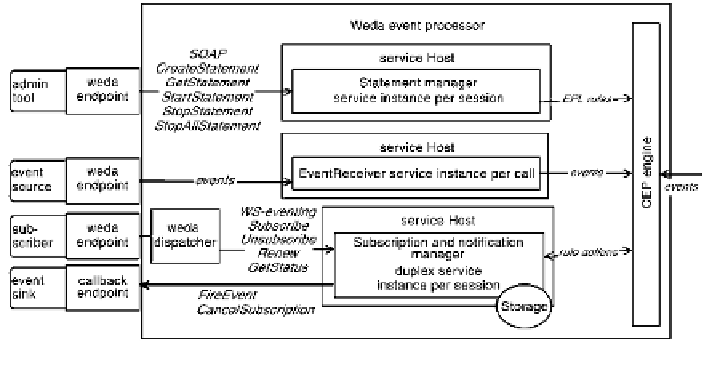
As shown in Fig.
7
, the Weda event processor consists of a dispatcher component,
four event processing services which can be running on separate instances and one
CEP engine. Complex event processing is technology to transform single, low-level
events into aggregated, high-level events by looking across event streams. Many
message types are transmitted here as SOAP management operations, events, sub-
scription messages, registered EPL rules and rule actions. Implementation of
eventing enhancements is now integrated in an experimental system only. After
Fig. 7 High-level process view of Weda event processor and its relationship to EDA components
Search WWH ::

Custom Search