Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
is produced. Aerogels can have pore volumes as large as 98% and
densities as low as 80 kg/m
3
[5]. Photographs of an aerogel are given in
the colour section (see Figure 3 in colour section). Owing to their high
porosity, aerogels are the lowest density solid materials in the world,
making them very good for thermal insulation when sandwiched between
glass plates and evacuated. NASA uses them to catch tiny meteorites
by attaching them to the outside of their spacecraft. However, for
biomedical applications, conventional sol-gels (xerogels) are of interest
and they will be the focus of this chapter.
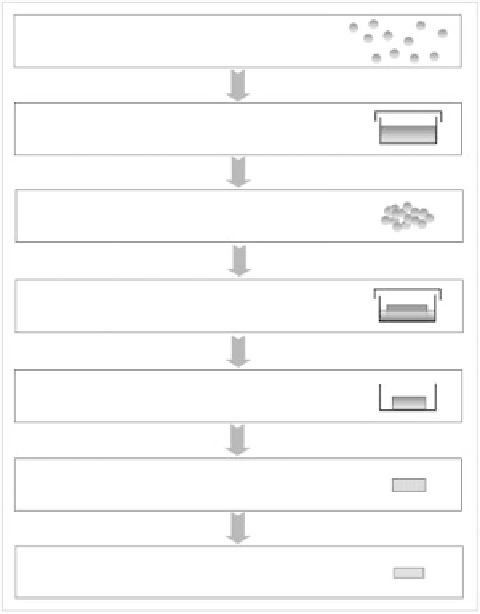
3.4 STEPS IN A TYPICAL SOL-GEL PROCESS
Each step of the acid-catalysed process will now be introduced. More
detail can be found in [1]. A schematic of the process can be seen in
Figure 3.2.
Stage 1
:
Mixing
precursors
+
catalyst
Hydrolysis & condensation to produce sol
Stage 2
:
Casting
into air-tight mould
Stage 3
:
Gelation
-network formation
Stage 4
:
Ageing
-strengthening
Stage 5
:
Drying
-removal of byproducts
Stage 6
:
Stabilisation
-removal of
nitrates/silanols
Stage 7
:
Densification
-removal of pores
Figure 3.2
A flow chart of the seven stages for the sol-gel synthesis of a glass (acid
catalysis).