Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
500
μ
m
Figure 12.15
Three-dimensional X-ray microtomography image of a sol-gel foam
hybrid. (Image by Sheng Yue. Copyright (2012) Sheng Yue.)
γ
can be functionalised and incorporated. An example is poly(
-glutamic
γ
γ
acid) (
-PGA
is synthesised by a biotechnology route, that is, produced by bacteria.
Another popular natural polymer is chitosan, a polysaccharide derived
from crustacean shells, which contains -OH and -NH
2
groups.
Class II hybrids of silica-gelatin, silica-
-PGA), which is a much simpler polypeptide than gelatin;
-PGA and silica-chitosan
have been produced with several methods of adding calcium. They
have also been foamed to produce porous scaffolds (Figure 12.15). A
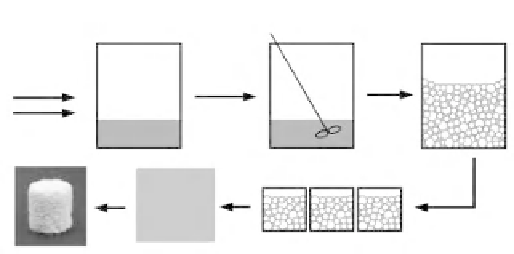
schematic of the process is shown in Figure 12.16. In some processes,
drying is carried out at low temperatures; in others, (preferably) freeze
drying quickly removes the water and other by-products of condensation.
Scaffolds can be made with stiffnesses ranging from that of a polymer to
that of a glass, or anywhere in between, by controlling the percentage of
γ
Sol
preparation
Vigorous
agitation
Bubble
stabilisation
Alkylsilane
surfactant
HF
H
2
O
+
polymer
sol
Freeze
Drying
Casting
Gelation
Figure 12.16
A schematic of the sol-gel foaming process for hybrids.