Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
where the membership function of the image
is given by
(3.11)
The above equation is defined for a discrete-valued function
f,
if the function
f
is a
continuous-valued then the max operator is replaced by the Sup (supremum) operator (the
supremum is the least upper bound) (Ross, 1995).
Implementation of the Extension Principle by !-cut method
The direct application of the Extension Principle very often involves a computationally
intensive procedure. Therefore, it is generally carried out in practice using the so-called
!-cut
method. By considering the fuzzy variable at a given
!
-cut level (see Appendix I),
operations on fuzzy sets can be reduced to operations within the interval arithmetic
(Dubois and Prade, 1980). The procedure of the implementation of the Extension
Principle by the
!
-cut method can be explained as follows:
1. Select a value of
!
[0,1] of the membership function (the
!
-cut level).
2. For the given value of a find the lower bound
and the upper bound
of
X
(x
i
)
=
!
"
(see Fig. 3.1)
.
3. Find the minimum and maximum values of
f
(
x
1
,…,
x
n
), considering all possible
values of
X
i
located within the interval
each
fuzzy variable
X
i
for which
thus determined are the lower and upper bounds of the output
Y
for the given
!
-cut. That
is,
The minimum and maximum
(3.12)
(3.13)
The membership function of
Y
satisfies
(3.14)
4. Repeat Steps 1 to 3 for various values of
!
to construct the complete
membership function of the output
Y
(see Fig. 3.2).




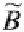



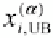
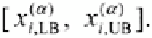
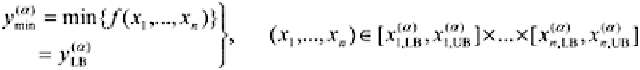


Search WWH ::

Custom Search