Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
(3.8)
where
Var(Y)
i
is the variance in
Y
due to the variance (uncertainty) in the input variable
X
i
. The standard FOSM method uses Equations (3.5) and (3.8) for the computation of the
mean and variance, respectively, of the output variable when the input variables are statistically
independent.
Although the method is simple and widely used, it suffers from some disadvantages
(see Subsection 4.2.2). As a result of the present research an improvement has been
applied to the conventional FOSM method. The result is an Improved FOSM method
(Maskey and Guinot, 2002 & 2003), which is an original contribution of the present study
and is described in detail in Section 4.2.
3.2
Fuzzy set theory-based methods
Uncertainty assessment is one of the various applications of the fuzzy set theory. Two
methods of uncertainty assessment based on fuzzy set theory are discussed in this section:
the Extension Principle-based method and the expert judgement-based qualitative method.
3.2.1
Fuzzy Extension Principle-based method
The fuzzy Extension Principle provides a mechanism for the mapping of the uncertain pa-
rameters (inputs) defined by their membership functions to the resulting uncertain output
(dependent variable) in the form of a membership function. First developed by Zadeh (1975)
and later elaborated by Yager (1986) this principle enables us to extend the domain of a function
on fuzzy sets, which is the basis for the development of fuzzy arithmetic. In order to define this
principle mathematically, consider a function of several uncertain variables
X
1
,…,
X
n
as:
Y
=
f
(
X
1
,…,
X
n
)
(3.9)
Let fuzzy sets
Ã
1
,…,
Ã
n
be defined on
X
1
,…,
X
n
such that
x
1
X
1
,…,
x
n
X
n
. Equation (3.9)
is identical to Equation (3.4), except that the uncertain variables in Equation (3.9) are
fuzzy, instead of random in Equation (3.4).
The mapping of these input sets can be defined as a fuzzy set
(3.10)






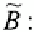

Search WWH ::

Custom Search