Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
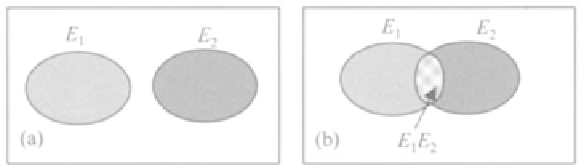
Figure 2.2
. Venn diagram of (a) mutually exclusive events, and (b) intersection
of two events.
Subjective or Bayesian view of probability
In the subjective view, probability is used as a belief. An event is a statement and the
(subjective) probability of the event is a measure of the degree of belief that the subject
has in the truth of the statement. The basic idea in the application of this approach is to
assign a probability to any event on the basis of the current state of knowledge and to
update it in the light of the new information. The conventional procedure for updating a
prior probability in the light of new information is by using Baysian theorem.
Bayes' Theorem is named after Thomas Bayes, an 18
th
century mathematician
(1702-1761) who derived a special case of this theorem. Bayes' theorem provides a rule
for updating the belief in a hypothesis
H
(i.e. the probability of
H
) given additional
evidence
E
and background information (context)
I,
as
(2.6)
The left hand-side term,
P(H|E,I),
is called the
posterior
probability and it gives the
probability of the hypothesis
H
after considering the effect of evidence
E
in the context
I
.
The
P(H|I)
term is just the
prior
probability of
H
given
I
alone; that is, the belief in
H
before the evidence
E
is considered. The term
P(E|H,I)
is called the likelihood, which
gives the probability of the evidence assuming the hypothesis
H
and background
information
I
is true. The denominator of the right-hand term,
P(E|I),
is the prior
probability of the evidence that can be regarded as a normalising or scaling constant. This
normalising constant is obtained by evaluating the exhaustive and exclusive set of
evidence scenarios (Hall, 1999):
(2.7)
The Bayesian theorem (Equation (2.6)) actually comes from a simple consequence of the
definition of conditional probability. The conditional probability of two sets provides the
dependency relationship between them. Given two sets
A
and
B,
the conditional
probability states that


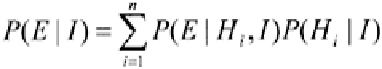
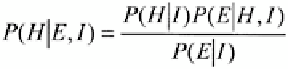
Search WWH ::

Custom Search