Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
Appendix I
FUZZY SETS, FUZZY ARITHMETIC
DEFUZZIFICATION
AND
I.1
Definitions on fuzzy sets
Fuzzy set theory has been introduced in Subsection 2.3.2. Definitions on some more
terminologies used in the fuzzy set theory are presented here. More detailed coverage of
this topic can be found in Bardossy and Duckstein (1995), Dubois and Prade (1988),
Kaufmann and Gupta (1991), Ross (1995) and Zimmermann (1991).
Fuzzy set
Let
X
be a universe set of
x
values (elements). Then
A
is called a fuzzy (sub)set of
X,
if
A
is a set of ordered pairs:
(I.1)
where
"
A
(x)
is the grade of membership (or degree of belief) of
x
in
A
. The function
"
A
(x)
is called the
membership function
of
A
.
Height of a fuzzy set
The
height
of a fuzzy set is the maximum value of the membership in its membership
function, i.e. the height of the fuzzy set
A
(I.2)
Support of a fuzzy set
The
support
of the membership function of a fuzzy set is the region of the universe that
is characterised by nonzero membership in the fuzzy set, i.e.
Supp(A)
={
x|"
A
(x)
>0}
(I.3)
Normal fuzzy set
A fuzzy set which has at least one element with unity membership is called a
normal
fuzzy set, that is, there exists
"
A
(x)
=1 for some
x X
. In terms of the height of the fuzzy
set, a normal fuzzy set has
h(A)
=1. If the height of a fuzzy set is less than unity the fuzzy
set is called a subnormal.


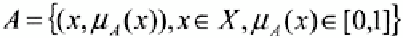

Search WWH ::

Custom Search