Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
where
Q
1
,…,
Q
4
are defined as follows:
(6.7)
Here, the integer value
n
and the residual fraction
r
are defined as
(6.8)
(6.9)
6.1.2
Sources of uncertainty
The various sources that lead to the uncertainty in the forecasts from the model discussed
above are identified as follows:
1. Water level measurements
2. Rating curve conversions
3. Propagation model
4. Other sources due to the ignored processes in the conceptualisation of the model.
The observed water levels at various time and locations are the only inputs to this model.
Therefore, the uncertainty due to the imprecise measurement of water levels is the input
uncertainty for this model. The uncertainty due to the rating curve conversions and the
process of propagation are considered as parameter uncertainty. The uncertainty due to
the ignored processes in the conceptualisation of the model is referred to here as other
sources. They are the ignored effects such as the interaction with confluences, the
attenuation of the flood wave and so forth.
Contrary to the rainfall-runoff type model presented in Chapter 5, in the present model
the uncertainty due to the uncertainty in the inputs is not very significant. This is due to
the facts that, in this particular model, the inputs are all measured (not forecasted) and
that the water level measurements are reasonably precise. According to the information
provided by the DIREN Centre in Orleans (France), the accuracy of the gauges for water
level measurement is ±1 cm. Also the calibration of the gauges has been done recently
and properly. The sources of uncertainty in the propagation of the flow and in the stage-
discharge conversions are the major sources of uncertainty for this model.
Pre-established rating curves, which are revised every two years, are used. The
conversion from water level to discharge is done using rating curves constructed from
regular sampling measurements. The uncertainty due to water depth to discharge
conversion can be particularly significant for high water levels when the extrapolation of
the curve is required.





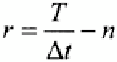

Search WWH ::

Custom Search