Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
1. Random selection of the initial population,
2. Selection for mating,
3. Crossover, and
4. Mutation.
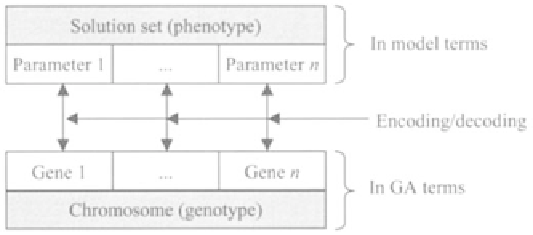
The initial population consists of sets of randomly selected solutions. A given solution
set (set of parameters) is an individual in GA terms. An individual is represented by a
chromosome set (also called strings) in GA operations. Chromosomes are made up of
genes, like a solution set consists of parameter values. Thus, while parameters and
solution sets are used in model terms, genes and chromosomes (also strings) are used in
GA terms. Encoding and decoding are the processes to convert a solution set to strings
and vice versa. Figure 5.6 illustrates the correspondence between model and GA terms.
Figure 5.6.
Model terms and GA terms for an individual of a population
The selection is a process in which parents (in pairs) are chosen from among individuals
of the population for mating. The selection is made according to their objective function,
popularly known as
fitness
function, values. The selected pairs (parents) from the mating
pool are then crossed over (hence the process is called
crossover
) to produce new
individuals
(offspring),
with a hope that the fit parents will produce even better fit
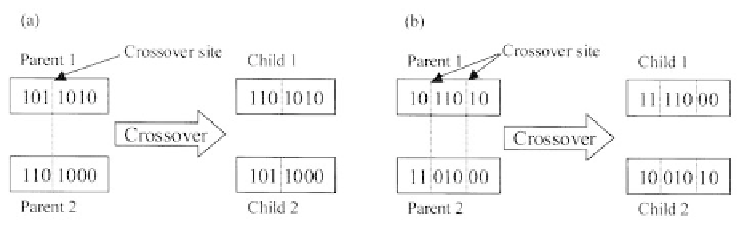
children. Examples of one-point and two-point crossovers by bits-exchanges are shown
in Figure 5.7. The offspring may also mutate.
Mutation
refers to the random distribution
Figure 5.7.
Examples of one-point (a) and two-points (b) crossovers. The
crossover sites chosen are arbitrary.

Search WWH ::

Custom Search