Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
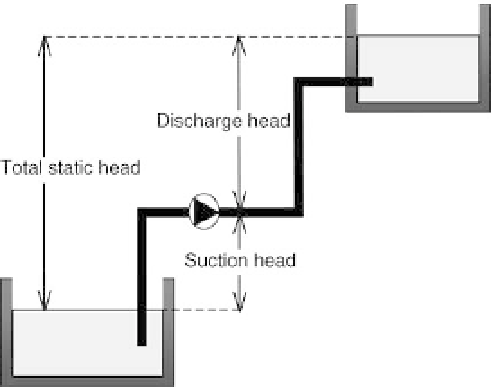
8.8
Total static head.
Two main pump groups can be distinguished among those utilised in biogas
plants: centrifugal and displacement pumps. Centrifugal pumps are used for
liquid substrates with dry matter content less than 8%, which is typically the
case for slurry. These pumps are robust and can generate pressures up to
20 bar, but the conveying capacity is strongly dependent on pressure losses
due to the head and friction. In the case of fibrous substrates such as straw,
centrifugal pumps can be equipped with cutters for breaking down the fibres
and thus preventing clogging. A weak suction head is a disadvantage of this
pump type.
Displacement pumps are used for substrates with a higher dry matter
content. They can convey material forwards and backwards, and their
conveying capacity is much less dependent on head and friction. Eccentric
screw pumps, also called progressive cavity pumps, are one type of these
pumps. They function with a metallic rotor in the form of a helix, which
turns eccentrically in a stator with a twin helix. Material can be transferred
at very low flow rates, although high pressures can be generated. A
disadvantage is their sensitivity to impurities, fibres or idle running. Another
type of displacement pump is the rotary lobe pump. Material is trapped in
the cavity of the lobes and is displaced as they rotate. These pumps are
resilient to impurities and fibres and so are frequently used in biogas
installations.
8.4.3 Valves
Valves are used for regulating, directing or controlling the flow. Depending
on the flow media and the specific requirements, different valve types are
employed. The main valve types used in biogas plants are gate valves,
butterfly valves and check valves.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search