Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
transition towards a biobased economy are triggering new opportunities for
AD (Ahring and Westermann 2004; Holbein and Layzell 2004; Mata-
Alvarez et al. 2000; van Dam et al. 2005; Verstraete et al. 2004). AD is seen
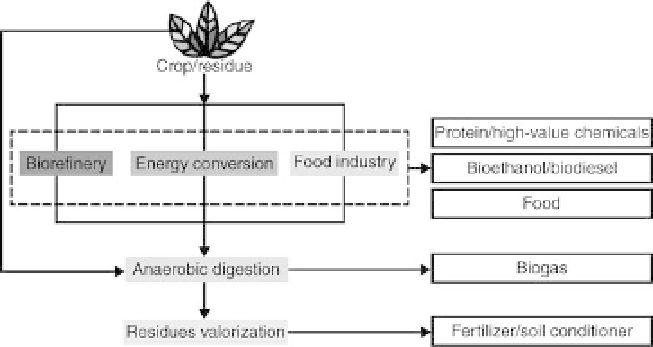
to increase its contribution to the biomass chain in two possible ways (Fig.
7.1).
Firstly, AD could be used to directly convert crops into methane as it has
been recognized that the technology is competitive in efficiencies and costs
to processes yielding other biomass energy forms including heat, synthesis
gases and ethanol (Chynoweth et al. 2001). AD has also been recognized to
be less demanding in resources such as water, nutrients and fossil energy as
compared with the more popular biofuel options like biodiesel or
bioethanol. In a research studying possible self-sufficiency at farm level in
Sweden, the use of biogas was favored over the other two options in terms of
its low relative need for arable land, concomitantly resulting in smaller
emissions from soil to air and water (Fredriksson et al. 2006).
Secondly, new residues (i.e. raw materials for AD) will be generated by
other bioprocesses in the form of either diluted waste streams with
important organic load or complex solid or semi-solid materials. Here, the
flexibility and simplicity of the AD process can add to the economic and
environmental sustainability of the entire chain by decreasing waste via the
production of additional energy carriers in the form of methane. In
addition, AD contributes to closing nutrient and carbon cycles at farm level
by means of the reuse of the residual digestate as soil conditioner and the
potential recycling of plant nutrients as NH
4
+
and PO
4
3
in the digestate
liquid or bound to the stabilized fibers in the digestate solids.
In the following sections, a framework for understanding the role of AD
within biomass chains is provided. Following that, examples are given
7.1 Possible biogass cascade configurations having anaerobic
digestion as a key element.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search