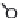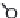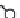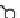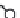Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
Queen Mother
Drone Mother Queens
A
B
C
D
Queens of
Test Colonies
Workers
A
B
C
D
A-D
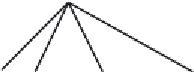
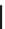
Figure 4.6.
A cross designed to test the ef ects of genetic diversity.
source combinations tested (two to six), resulting in much less poten-
tial genetic variation compared with open-mated queens, small sample
sizes, or both.
h e best demonstrations of the ef ects of multiple mating are those
of Heather Mattila. She and her collaborators set up colonies with
queens that had been inseminated with just one male or with a pooled
and mixed combination of 15 males. All queens received the same
amount of semen during instrumental insemination. Drones were
drawn at random from a pool of about 1,000 drones from 11 source
colonies. Altogether, 12 genotypically diverse and 9 genotypically less
diverse (single-male) colonies were tested. Colonies were set up as
swarms and were allowed to build up and make it through the winter.
h ey were fed antibiotics to control for any ef ects of genotypic diver-
sity on parasite and pathogen loads in the colonies. Colonies with poor
brood viability were removed, a control for the production of diploid
males. h e results were clear: the more genotypically diverse colonies
built up their colonies faster (combs, food, and bees), had more forag-
ing activity, stored more food, had more adult workers, survived the
winter better, and raised more reproductive males. h e success of this