Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
global network (e.g. Internet). Let
s
0
,s
1
, ..., s
m
be gateway addresses for seg-
ments
S
0
,S
1
, ..., S
m
. Let workstations interconnect via a virtual private network
(VPN). If some data from a workstation with address
a
in segment
S
i
needs to
be transferred to a workstation with address
b
in segment
S
j
, the transmission
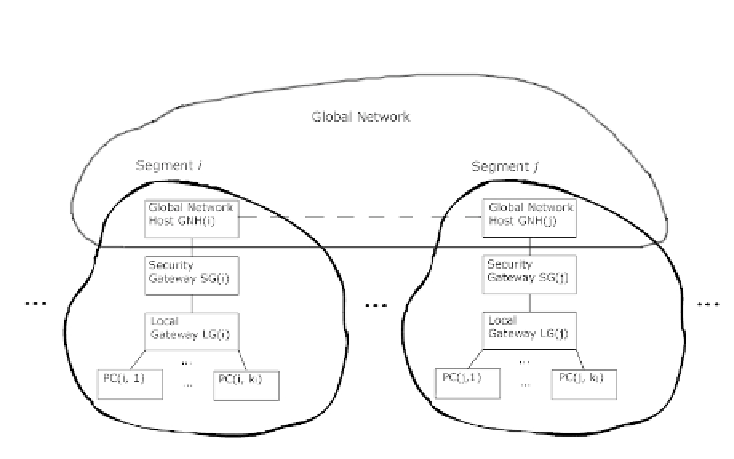
is performed in the following way (fig. 1):
Fig. 1.
System model
- the data from workstation
a
is first transferred to a Local Gateway LG(
i
)in
S
i
;
- then data is passed to a Security Gateway SG(
i
). Security Gateway operates
as a PROXY server - it connects to workstation
a
, gathers data for work-
station
b
, and collects data packets from
S
i
segment in a queue according to
their arrival time. Then data is encrypted with a key of SG(
j
) - the Secu-
rity Gateway of data recipient segment. Then SG(
i
) connects to SG(
j
)and
transfers encrypted data:
•
SG(
i
)passesdatatoaGlobalNetworkHostGNH(
i
),whichinturn
passes data to a corresponding host GNH(
j
)viaaglobalnetwork;
data is then passed to SG(
j
). SG(
j
) collects packets for
S
j
segment and
stores them in a queue.
- Packets in a queue are decrypted, SG(
j
) connects to a workstation
b
and
transmits data via the internal gateway LG(
j
);
-LG(
j
) sends data to workstation
b
in
S
j
segment.
•
Every segment
S
0
,S
1
, ..., S
m
contains software and/or hardware adversary
agents. To work properly these agents need to receive some instructions from
an adversary agent in a global network (AGN). Let us consider that AGN is in
total control of GNH(
j
),
j
=0
,
1
, ..., m
, and adversary agents in
S
0
,S
1
, ..., S
m