Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
quality of the
DoS
attack detection
is increased. The same is valid for
other alert correlation classifiers.
6 Conclusion
Though intrusion detection task is
being a subject of intensive re-
search during at least the last dec-
ade, it remains to be a problem;
many important issues and peculi-
arities of this task have not been
investigated in depth. One of the
remarkable drawbacks of the ex-
isting approaches is simplified
modeling of input data used in de-
velopment of IDS. Indeed, along
with multiplicity and heterogeneity of data sources to be taken into account, several
other specific features of the intrusion detection system input are critical to fill in the
gap between existing models used in IDS and reality. Among these features, temporal
nature, high-frequency dynamics and asynchronous nature of input are of the primary
importance.
These factors result in the necessity to account such an important issue as
information ageing caused by the fact that input data streams arrive in IDS with vari-
ous averaged frequencies and asynchronously.
The input data model considered in this paper takes into account the aforemen-
tioned factors. For such model of IDS input, the paper proposes an approach called
heterogeneous alert correlation. The major idea of the approach is to organize IDS
system as a structured set of interacting classifiers dealing with data received from
various data sources. The first layer of this structure is composed of classifiers operat-
ing with inputs of particular data sources. Each of them is trained for detection of at-
tacks of a fixed class (in the developed IDS software prototype, the attack classes
DoS
,
Probe
, and
U2R
are considered). Each of such specialized classifiers produces
decisions of two types: "
Alert
" in regard to the particular class of attacks (e.g. "
DoS
alert
", "
U2R alert
", etc.) or "
Normal
". A peculiarity of such classifiers operation is
that they produce decisions in different time instants. These decisions asynchronously
arrive at the second layer responsible for correlation of the alerts produced by the first
layer classifiers trained for detection of the attacks of the same class. In turn, the re-
sults of the alert correlations produced by the specialized classifiers of the second
layer are asynchronously forwarded to the top layer. The top-layer classifier solves in-
trusion detection task: it combines heterogeneous alerts of specialized alert correlation
classifiers and combines them producing decision it terms of particular attack class.
Two theoretical problems should be solved to implement the described approach:
(1) development of data ageing model; and (2) development of specific techniques to
train alert correlation classifiers to make decisions based on asynchronous input. In
the developed IDS prototype the solutions proposed by the authors in previous re-
search are used [5, 8]. This approach was implemented within multi-agent IDS
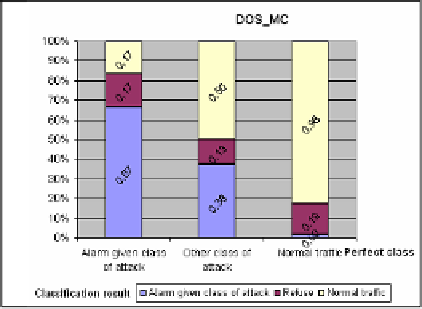
Fig. 8.
Evaluation of the performance quality of the
DOS_MC
meta
-
classifier