Geology Reference
In-Depth Information
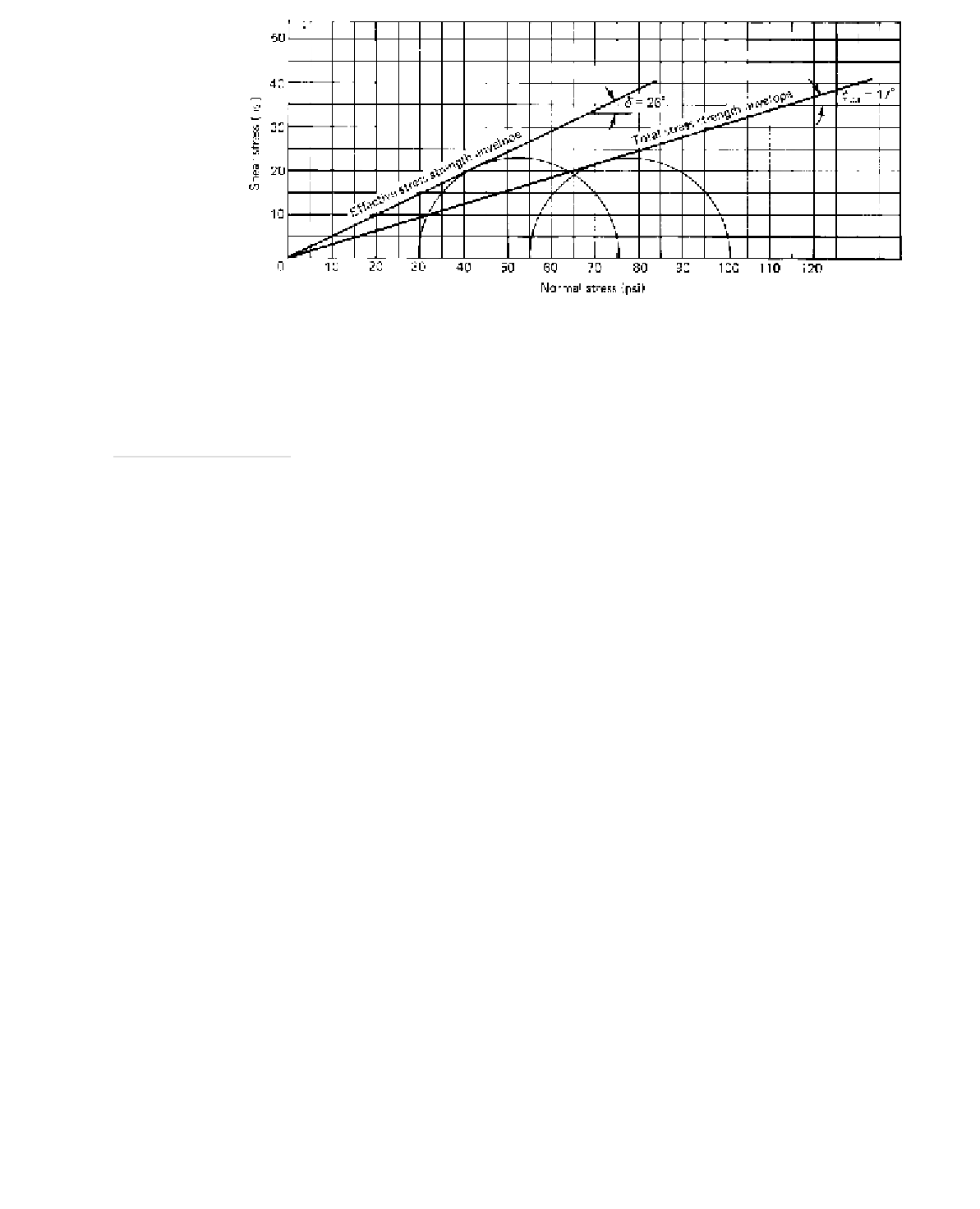
Figure 22-11
Results of CU Test for Given Numerical Example
As indicated previously, values of the angle of internal friction and
cohesion are the major results of a triaxial test. In addition to these
parameters, however, reports should include values of the initial unit
weight, moisture content, and degree of saturation, as well as the
height-to-diameter ratio of the specimen tested. The type of test per-
formed (UU, CU, CD) and the type (undisturbed, remolded, compacted)
and shape (cylindrical, prismatic) of specimen should also be reported.
Of course, a visual description of the soil and any unusual conditions
should be noted. The average rate of axial strain to failure, the axial
strain at failure, and whether strain control or stress control was used
should also be indicated. The stress-strain curves, pore pressure-strain
curve (if the CU test is performed), and shear diagram (Mohr circles)
should be presented in the report. Sketches of the failed specimen
might also be included.
For any dry soil, about the same shear strength parameters would
be obtained from any of the three triaxial tests (UU, CU, or CD). For a
saturated or partially saturated cohesionless soil, the CD test will yield
about the same
SUMMARY
angle as for a dry soil, unless the material is very fine
grained (low permeability) and/or the test is performed at an extremely
rapid rate of strain. For any saturated cohesive soil, results are dependent
on which of the three tests is used. Parameters will range from
0 and
c
0 using the
CD test. Results will also depend on whether the soil is normally consol-
idated, overconsolidated, or a remolded sample. For any partially satu-
rated cohesive soil, results depend on both degree of saturation and type
of drained test performed. Results from an undrained test will be highly
dependent on the sample's degree of saturation, ranging from
some value using the UU test to
true value and
c
0 for
S
100% to
true value for
S
0 [1].

Search WWH ::

Custom Search