Geology Reference
In-Depth Information
cohesive soils. Methods of correcting
N
-values and correlations between
SPT
N
-values and several soil parameters are available in
Soils and
Foundations
7
th
edition, by Liu and Evett (Prentice Hall, 2008).
The reader is cautioned that, although the standard penetration
test is widely used in the United States, results are highly variable and
thus difficult to interpret. Nevertheless, it is a useful guide in founda-
tion analysis. Much experience is necessary to properly apply the results
obtained. Outside the United States, other techniques are used. For
example, in Europe the cone penetration test is often preferred.
The cone penetration test (CPT) has been widely used in Europe for
many years but is now gaining favor in the United States. It has the
advantage of accomplishing subsurface exploration rapidly without
taking soil samples.
In simple terms, a
cone penetrometer
is a slender metal rod con-
taining a 35.7-mm-diameter, cone-shaped tip with a 60° apex angle; a
friction-cone penetrometer
contains a 133.7-mm-long cylindrical sleeve
in addition to a cone-shaped tip. A penetrometer is advanced into and
through the soil, and its resistance to being advanced through the soil
is measured as a function of the depth of soil penetrated. Correlations
between such resistance and soil types can give valuable information
regarding soil type as a function of depth. Cone penetrometers can be
categorized as mechanical cone penetrometers (ASTM D 3441) and elec-
tric friction-cone penetrometers (ASTM D 5778).
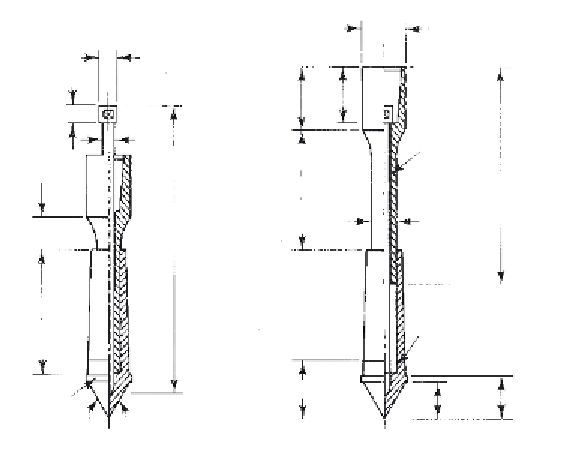
There are two types of mechanical cone penetrometers—the
mechanical cone penetrometer
(Figure 2-8) and the
mechanical friction-
cone penetrometer
(Figure 2-9). The main difference between the two is
that in addition to cone resistance, the friction-cone penetrometer also
allows for determination of side (sleeve) resistance as the penetrometer
is advanced through the soil. Mechanical cone penetrometers are either
pushed (by a hydraulic jack, for example) or driven (such as by blows of
CONE
PENETRATION
TEST (ASTM
D 3441 AND
D 5778)
Figure 2-8
Mechanical Cone
Penetrometer Tip
(Dutch Mantle
Cone): (a) Collapsed;
(b) Extended.
Source:
Annual Book of
ASTM Standards, ASTM,
Philadelphia, 2007.
Copyright American Society
for Testing and Materials.
Reprinted with permission.
35.7 mm
15 mm
52.5
mm
15 mm
12.5
mm
14 mm
179.5 mm
92 mm
23 mm
21 mm
230 mm
99 mm
32.5 mm
47 mm
30
mm
35 mm
35.7 mm
60˚
(a)
(b)



Search WWH ::

Custom Search