Geology Reference
In-Depth Information
(1) through (6) in the “Procedure” section] without using a calibra-
tion curve, and the other specimen is tested in accordance with
ASTM Test Method D 2216 (Chapter 4).
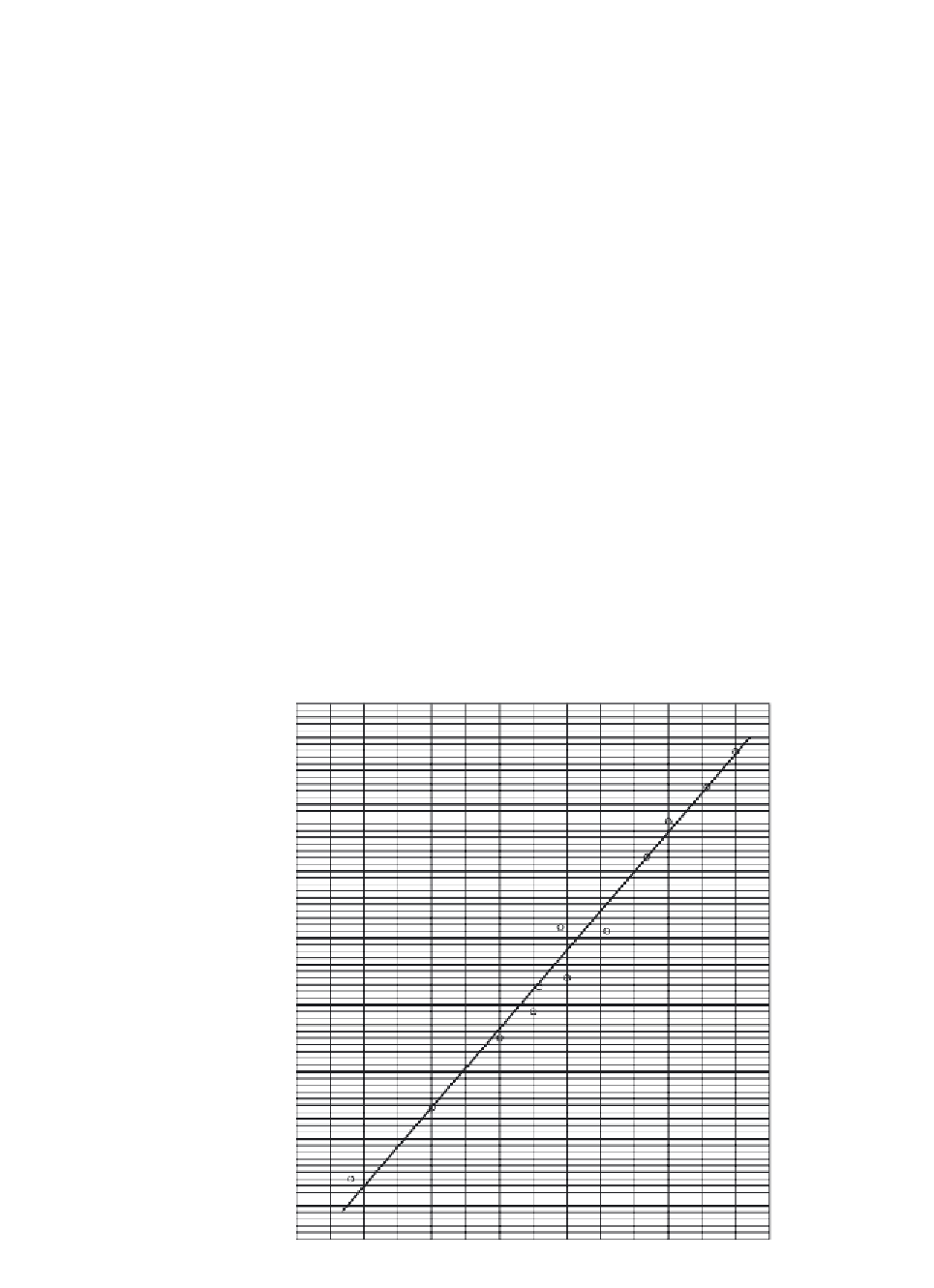
(4) The results of the oven-dry water content determined by Test
Method D 2216 from all the selected samples are plotted versus
the gage reading from the calcium carbide tester for the corre-
sponding test specimen pair. A best fit curve is plotted through the
points to form a calibration curve for each soil type. Comparisons
should be relatively consistent. A wide scatter in data indicates
that either this test method or Test Method D 2216 is not appli-
cable to the soil or conditions. Figure 13-2 shows a typical cali-
bration curve.
(5) A comparison of this test method with Test Method D 2216 for
a given soil can be made by using the calibration curve. Points that
plot off the curve indicate deviations. Standard and maximum
deviations can be determined if desired.
The general procedure for determining moisture content by means of a
calcium carbide gas moisture tester is to place a measured volume of cal-
cium carbide in the testing apparatus along with two steel balls and a
PROCEDURE [1]
Figure 13-2
Typical Calibration
Curve [1]
CALIBRATION CURVE
CALCIUM CARBIDE TESTER NO.
721915
4
5 6 7 8 9 101112131415161718
DIAL READING CALCIUM CARBIDE TESTER



Search WWH ::

Custom Search