Database Reference
In-Depth Information
Utilities.
Database administrators use a comprehensive suite of utility programs to
perform their maintenance and tuning functions.
DB tools.
Programmer/analysts make use of query and reporting tools to create
components of applications. Power users and specialized users create their own
queries and reports with the aid of these tools.
INSIDE A DBMS
We have discussed the significance and capabilities of the database manage-
ment system (DBMS). You know that it is a collection of specialized software
modules. Database administrators cannot implement, control, and manage data-
bases without the DBMS. Every request for data from the user groups must go
through the DBMS. Power users need the facilities of the DBMS to create and run
their database queries. DBMS stands in the center of an organization's database
environment.
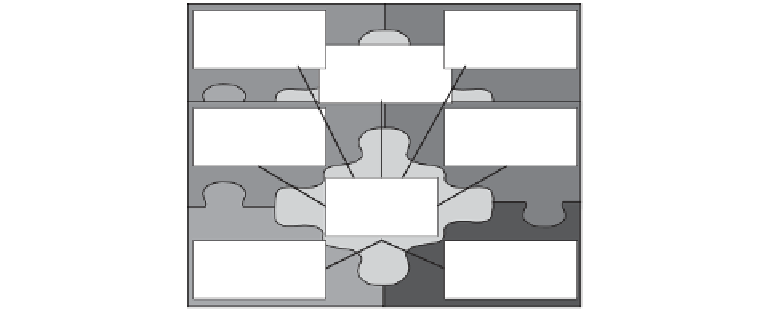
Let us now take a look inside the DBMS. Let us find out what components form
the software collection and examine each component. Over the years, the features
and functions of DBMSs have been broadened. Today's DBMSs do not just provide
data access; they contain a powerful and versatile set of tools. Making the toolkit a
part of DBMSs is a major step forward. Figure 2-8 shows how the various software
modules inside a DBMS may be grouped as major components. We will study each
of these components.
Database Engine
The kernel or heart of the DBMS is the database engine. From this central posi-
tion, the database engine coordinates all the other components. When you review
every other component, you will note their specific tasks. The engine has the special
responsibility of coordinating the tasks performed by the other components.
Because of this coordination, every database operation gets completed correctly and
Commn.
Interface
Utility
Tools
Data
Dictionary
Application
Developer
Forms
Generator
Database
Engine
Query
Processor
Report
Writer
Figure 2-8
Inside a DBMS.

Search WWH ::

Custom Search