Database Reference
In-Depth Information
INTERNET
Internet
Clients
EXTERNAL
USERS
Local
Clients
Firewall
Web
Server
INTERNAL
USERS
Enterprise
Database
Application
Server
Database
Server
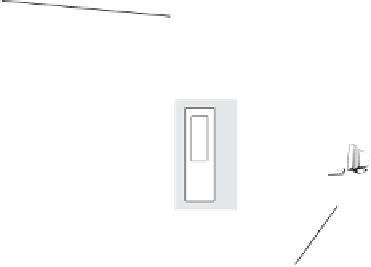
Figure 19-12
Intranet and firewalls.
Activity logging.
A good firewall system logs all successful and failed attempts
through it. This information is valuable for tracking any intruders and determining
the extent of any inflicted damage.
Alarm function.
In some firewall systems, the administrator can set an alarm to
trigger a special event if an intruder tries to gain access to sensitive data.
Firewall Filtering Techniques
The following are common techniques offered:
Packet filter.
Matches key fields within an IP packet against defined rules and either
passes the packet on or drops it. Dropped packets are discarded. Because packet
filters have no concept of the session, this method is vulnerable to spoofing. Also,
packet filters are difficult to configure.
Session filter.
Retaining information on all active sessions through the
firewall, a session filter determines whether packets flowing in the opposite
direction belong to an approved connection. A session filter also performs session
auditing.
Application-Level Gateway.
This is a mechanism to apply interception rules to spe-
cific applications such as Telnet or FTP services.
Circuit-Level Gateway.
This is a high-level protection mechanism applied when a
TCP connection is made. Once the connection is authorized, packets can flow
between computer systems without further verifications.
Wrappers
Although firewalls are effective in keeping intruders from outside, they
can do very little to prevent unauthorized access from within. Wrappers form the
























































Search WWH ::

Custom Search