Database Reference
In-Depth Information
EMPLOYEE
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
1
4
8
2
3
6
9
5
7
EXECUTIVE
MANAGER
STAFF
Figure 6-21
Exclusive subsets.
BANKING ACCOUNT
12
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
4
8
1
2
3
6
1
9
6
5
5
7
CHECKING
ACCOUNT
SAVINGS
ACCOUNT
LOAN
ACCOUNT
Figure 6-22
Nonexclusive subsets.
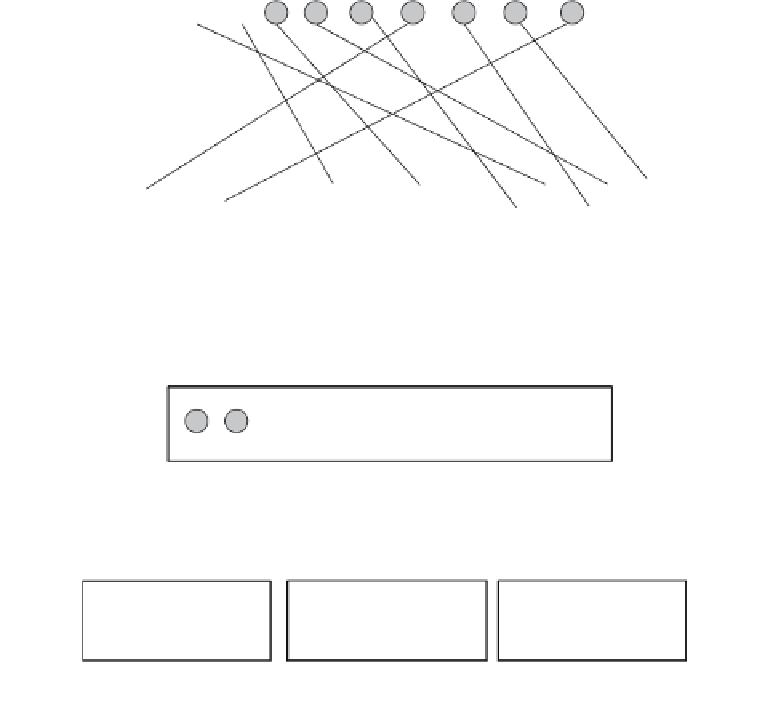
Total Specialization
Figure 6-23 illustrates the special case in which every
instance of the superset must be an instance of some subset. That means the list of
subsets is total or complete. The model includes all possible subsets known at the
time of design. Total specialization implies exhaustive specialization; all possible
subsets are considered.
Partial Specialization
Figure 6-24 shows an example of partial specialization.
Here, some instances of the superset are not found in any of the subsets. That means
that the list of subsets is not exhaustive; all possibilities are not accounted for in the
subsets. The list of subsets is only partial.
In a particular data model, you are likely to see combinations of these special
cases. The following are the possible combinations:
•
Exclusive, total specialization
•
Nonexclusive, total specialization













Search WWH ::

Custom Search