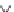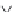Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
essential fatty acids (EFA) because mammals cannot synthesize them (Enser, 1984).
ALA and LA, which are the precursors for other PUFA that are both nutritionally and
physiologically important, can be converted to longer chain FA through desaturation and
elongation by specific enzymes (Figure 16.1). ALA can be converted to EPA (C20:5n-3)
and DHA (C22:6n-3), whereas LA can be converted to arachidonic acid (ARA; C20:4n-6)
(Kurlak and Stephenson, 1999). Thus, animals can obtain DHA and EPA either directly
from the diet or by
de novo
synthesis from dietary ALA. DHA is essential for normal
growth and development in the infant (Calder, 2003), and ARA is the major regulator
of intestinal homeostasis and repair following injury. Gastrointestinal disturbances rank
among the leading cause of neonatal morbidity and mortality (Jacobi
et al.
, 2011).
16.3.1
Sources of omega fatty acids
The FA compositions of different vegetable or fish oils are listed in Table 16.1. LA
(C18:2n-6) and ALA (C18:3n-3) can be obtained from grains and vegetable oils, whereas
EPA (C20:5n-3) and DHA (C22:6n-3) are predominantly found in many types of fish
oils, such as salmon, sardine, shark-liver, tuna and menhaden oils. Many vegetable oils,
such as soybean, corn and sunflower oils, are rich in n-6 FA, mainly as LA, but linseed
is a rich source of ALA (more than 50%). Walnut, canola or soybean oils also show an
ALA content ranging from 7 to 17%, which is considered an adequate source of n-3 FA.
Δ15 desaturase
Linoleic acid (C18:2n-6, LA)
Δ6 desaturase
α-linolenic acid (C18:3n-3, ALA)
Plant only
Δ6 desaturase
γ-linolenic acid acid (C18:3n-6, GLA)
Elongase
Stearidonic acid (C18:4n-3)
Elongase
Dihomo-γ-linolenic acid (C20:3n-6, DGLA)
Δ5 desaturase
Eicosatetranoic acid (C20:4n-3)
Δ5 desaturase
Arachidonic acid (C20:4n-6, ARA)
Eicosapentaenoic acid (C20:5n-3, EPA)
Elongase
Elongase
C22:4n-6
Docosapentaenoic acid (C22:5n-3, DPA)
Elongase
Elongase
C24:4n-6
C24:5n-3
Δ6 desaturase
Δ6 desaturase
C24:5n-6
β-oxidation
C24:6n-3
β-oxidation
C22:5n-6
Docosahexaenoic acid (C22:6n-3, DHA)
Figure 16.1. The conversion of n-6 and n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids of plant origin to their longer chain
form (redrawn from Tanghe and De Smet, 2013).