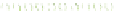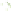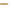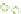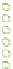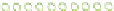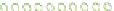Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Covalent bonds
Hydrogen
bonds
Lignin
Hemicelluloses
Cellulose
Lipophilic
interactions
(van der Waals)
Figure 6.3
Representation of LCC and its interaction with cellulose.
• the syringyl unit, derived from
trans
-sinapyl alcohol, which is present with the
guaiacyl unit in hardwoods; and
• the
p
-hydroxyphenyl unit, derived from the
trans-p
-cumaryl alcohol, which is
characteristic of grasses.
Lignin is linked through covalent bonds (ester and ether) to hemicelluloses. The
two macromolecules constitute the lignin-carbohydrate complex known as LCC.
As the hemicelluloses can be linked to cellulose through hydrogen bonding, the
LCC is capable of agglomerating around the cellulose microfibrils (Figure 6.3).
6.2.2
Hierarchical Structure of Wood and Timber
Employed for thousands of years as a structural material or a source of energy,
wood is still widely used as a construction material because of its mechanical
properties and its visual aspect. The diversity of wood species throughout the
world and the elevated world production levels make it an abundant material
available in almost all countries globally.
Wood is defined as the ligneous and compact material forming the branch, the
trunk and the roots of trees. Timber is the term dedicated to sawn wood, usually