Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
oils with vinyl monomers through cationic and free-radical polymerization to pro-
duce a broad range of thermosetting materials [14-18]. Under appropriate condi-
tions, virgin oils are cross-linked with styrene and divinyl benzene to produce
thermosets comparable to thermosets made from petroleum-based monomers
with glass transition temperatures ranging from 0 to 105°C, and moduli from 6
to 2000 MPa. These materials display characteristic behaviors, such as dynamic
mechanical properties, tensile stress-strain behavior, damping behavior, and shape
memory, comparable to materials from fossil-based monomers [19-22]. These
results emphasize that vegetable-oil-based materials are able to compete directly
with and replace materials derived from fossil-based monomers.
5.2.3
Epoxidized and Acrylated Epoxidized Vegetable Oil
Modifications to the double bonds in the vegetable oil triglycerides provide sites
with higher reactivity, offering more pathways to vegetable oil polymerization.
Epoxidized soybean oil and acrylated epoxidized soybean oil (AESO) are two
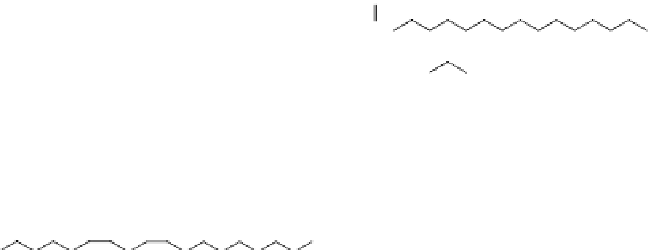
commercially available modified oils. Scheme 5.1 shows their modification
O
O
O
O
O
O
Soybean oil
Acidic environment
peroxide
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
Epoxidized soybean oil
Acrylic acid
O
O
O
O
OH
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
HO
O
O
Acrylated epoxidized soybean oil
Free radical mechanism
Cross-linked polymer network
Scheme 5.1
Modification pathway for AESO, which can be used to produce thermosetting
polymers [3, 7].