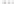
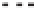
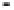
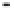
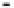
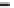
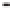
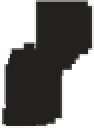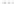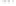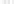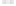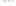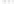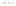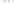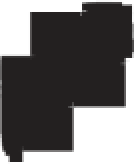Geology Reference
In-Depth Information
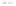
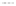
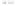
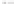
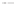
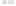
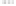
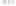
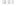
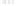
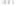
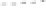
Rock types
native sulphur deposits with
some pyrite and marcasite
porphyry stock
Granodiorite
Hydrothermal
intrusion breccia
High-temperature fumarole
6
5
Bedded lavas and
pyroclastics
4
Pb - Zn
precious-metal
veins
Alteration
3
Silicification and
advanced argillic
Propylitic
2
1
Sericitic
Potassium
silicate
Pre-volcano
ba
sement
0
Sea level
-1
-2
PLUTON OF GRANODIORITE
-3
0
4 km
Horizontal scale (same as vertical)
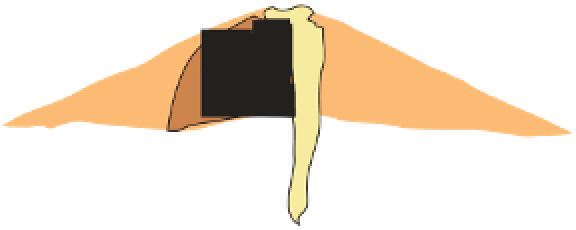
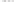
Figure 10.3
Summary of typical zones of wall-rock alteration that occur in and
around porphyry copper mineral deposits. Similar alteration zones can occur on
a much smaller scale around hydrothermal veins and fractures.
clastic sedimentary and volcanic lithologies, a 'border group' has been
mapped, comprising thin sills of fine- to medium-grained gabbro, norite and
pyroxenite. The vast bulk of the complex is divided into four zones on the
basis of rock-type and internal variations (Figure 10.5). The
lower zone
,
comprising thick, uniform orthopyroxenite layers, with interlayered olivine
pyroxenites and harzburgites, is overlain by a layer termed the '
critical zone
'
(so-called because of its content of chromium and hence its critical economic
importance), containing interlayered norites and anorthosites near the top with
anorthosite-norite-pyroxenite layers further down. Within the critical zone there
are several prominent chromitite layers, each up to 1.5 m thick, and many
smaller layers (Figure 10.6), and also sulfide segregations, including a layer