Geology Reference
In-Depth Information
3. Eutaxitic textures - these refer to textures formed in hot ignimbrites which
start to weld back together (see below) and include streaked out pumice
termed fiamme (Figure 5.12).
4. Fluidisation pipes - gas-escape structures, or fluidisation/fumarole pipes
found more commonly in thick, massive ignimbrite deposits. These vertical
columns or pipes contain lithic and coarse pumice fragments depleted of
fine ash by gas streaming through these localised zones, which also often
preferentially
cements
these
horizons
making
them
resistant
to
erosion
(Figure 5.13).
5. Vapour-Phase Crystallisation - a post-depositional process, where crystalli-
sation takes place in open spaces under the influence of a vapour phase.
Hot vapours, are generally enriched in H
2
O, CO
2
and SO
2
and Cooling of
these element-rich phases may result in the crystallisation of a variety of
minerals into open cavites.
Lithophysae
is a hollow, bubble-like structure
found within the cavities of pyroclastic flows, and in some examples a well-
cemented, white rock with little pore space known as
sillar
can develop and
may be associated with fluidisation pipes.
Probably the most important skill to work on when recording pyroclastic
deposits is the use of schematic and quantitative logs (for example, Chapter 2),
accurate grain-size information and a keen eye for sedimentary structures
(Figures 5.4 and 5.5). If you are working in such areas you can construct your
own log templates, use quadrant statistics and often trowels and small shovels
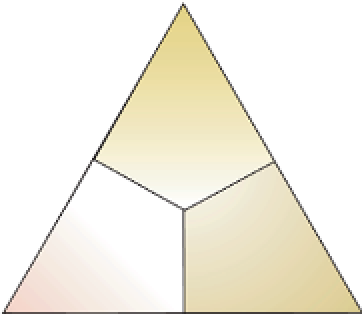
Pumice & Glass
vitric ash
vitric tuff
lithic ash
lithic tuff
crystal ash
crystal tuff
Lithics
(rock fragments)
Crystals
Figure 5.6
Classification based on the type of fragments present.