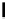Image Processing Reference
In-Depth Information
100,000
100,000
10,000
10,000
1,000
1,000
100
100
10
10
1
1
0
1
2
3 4 5
Transmission delay (ms)
6
7
8
9
10
0
1
2
3
4 5
Transmission delay (ms)
6
7
8
9
10
(a)
(b)
100,000
10,000
1,000
100
10
1
0
1
2
3 4 5
Transmission delay (ms)
6
7
8
9
10
(c)
FIGURE .
Measured WLAN-latency statistic ( byte every ms). (a) Reference measurement (no other fre-
quency user). (b) with WISA in parallel,
ms downlink influence clearly visible ( m distance). (c) same, but uplinks
only (downlink in cable); four consecutive WISA nodes ( events per second simultaneously)
+
28.5 Wireless Power Subsystem
Wireless power in principle can be supplied by different concepts:
•
Energy scavenging
: Taken from the local environment in the form of light, heat, and
vibration/motion
•
Energy storage
: Included in the system in the form of batteries, fuel cells, etc.
•
Energy distribution
: Transmitted to the system via optical or radio frequencies, sound, etc.
The use of battery power is considered acceptable in the consumer world. However, in general indus-
trial applications, where hundreds of devices require constant, reliable power supply and run day and
night, batteries are not an option. Their energy density (normally around . Wh
cm
for primary
batteries) is still too low, or the other way round the consumption of low power radios and sensors is
still too high for general use. While for secondary batteries, there has been quite some development
their volumetric energy density are still significantly lower than for primary batteries, typically by at
least a factor of -. For primary batteries, there has not been a noticeable progress regarding energy
density.
/