Image Processing Reference
In-Depth Information
Time
Frequency
Location
FIGURE .
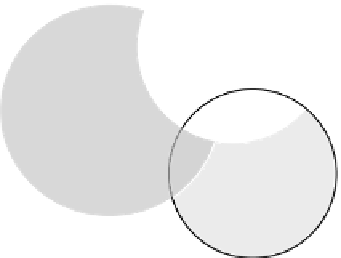
Coexistence issue occurs if there is a “hit” in time and frequency and location.
has to be announced in advance and released by a person/committee responsible for frequency use
allowance [,].
Wireless coexistence is an issue only if the same frequency is used at the same time and close by
(Figure .).
Separation in location is seldom a free parameter; therefore, time and frequency can be optimized.
If there would be an unlimited bandwidth available, simple frequency separation would be the
simplest approach. Nevertheless, the highway example shows that reserving a full lane of the highway
just for one vehicle type is generally not efficient. Many different vehicles may use the same lanes if
they have the ability to change lane and if on average a low duty cycle or low density of vehicles can
be guaranteed.
Separation in time, by low duty cycle, is exactly the approach being used in many wireless instal-
lations by frequency management, thus allowing many users with low duty cycle.
In practical applications, coexistence always has two aspects:
. Be robust against interference from other wireless users (low susceptibility).
. Efficient usage of radio frequencies (spectral efficiency and low duty cycle) to leave
enough free resources for other users.
WISA was designed to be robust by using adaptive retransmissions. Nevertheless, the continuous use
of a significant part of the frequency band by an unfriendly system with a high duty cycle and long
telegram lengths (longer than the maximum number of WISA retransmits) will make it impossible
for a WISA system to transmit its data within the time limit requirement (e.g., ms).
To discuss coexistence more quantitatively, characteristic numbers are helpful, which are defined
here as follows:
Robustness can be measured by the factor between the maximum to the minimum delay values,
measured in some defined coexistence test-setup.
Robustness
R
=
min. delay/max. delay
R
WISA
=
ms
/
ms
=
.
In an existing system between two user interfaces under idealistic and realistic but more worst case
conditions, e.g., the coexistence with other wireless systems in their typical channel occupation mode,
the more close to unity, the better is the robustness.