Image Processing Reference
In-Depth Information
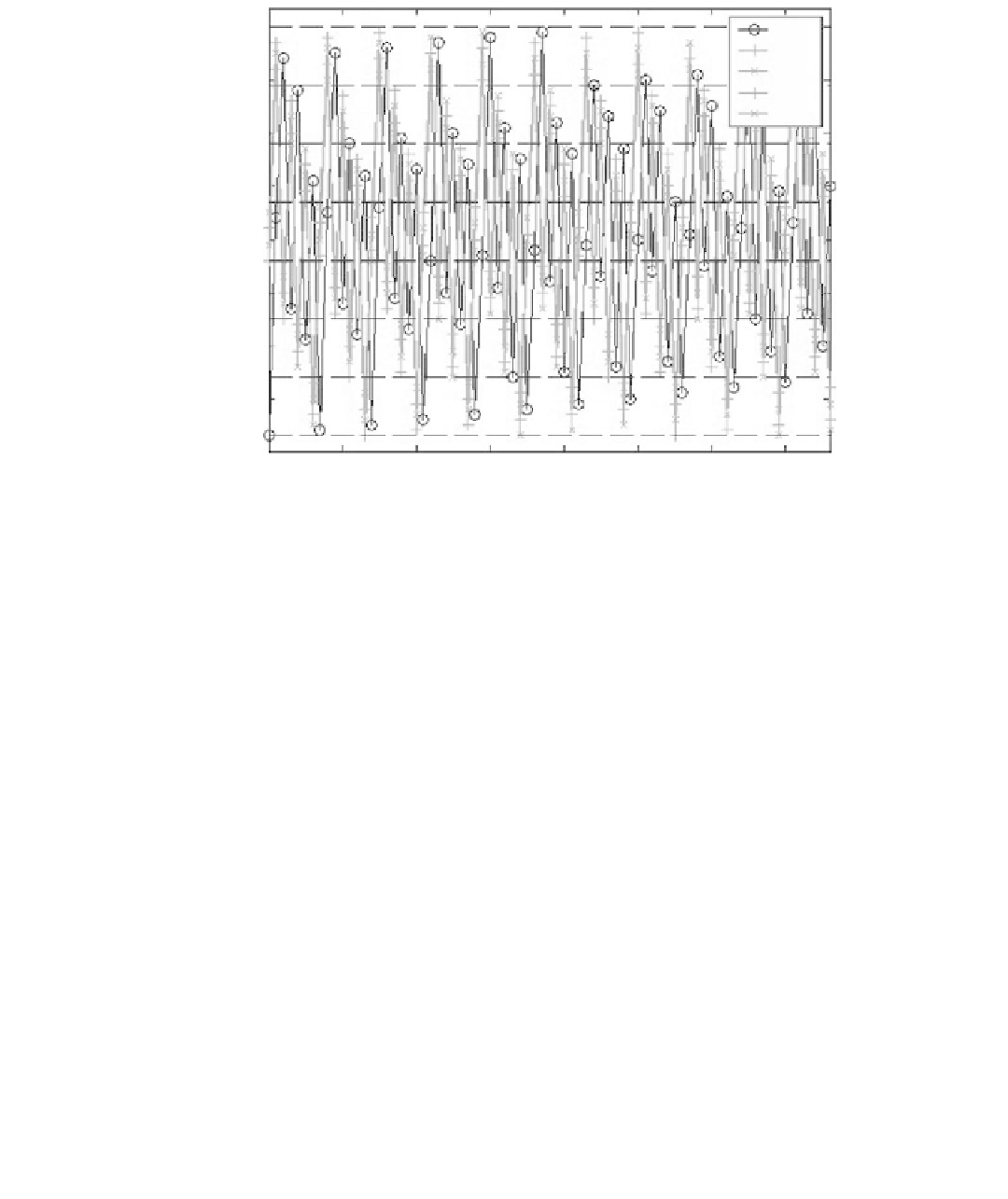
2480
DL
UL
1
UL
2
UL
3
UL
4
2470
2460
2450
2440
2430
2420
2410
2400
0
10
20
30 40
Frame number, FN
50
60
70
FIGURE .
). (From Schieble, G., Dzung, D., Endresen, J., and Frey, J.-E.,
IEEE Ind. Electron. Mag
., , , . With permission.)
Example FH sequences (cell_id
=
sequences has been studied in Ref. []. In general, there are a number of interference effects to be
considered:
•
Co-channel interference from same frequency transmissions becomes relevant if the C/I
ratio is below dB [] (distance effects).
•
Adjacent channel interference is relevant if the adjacent channel interference C/I ratio is
below
dB. his condition may well be true for colocated base stations.
•
Multiple interference from any of the five links.
•
−
of an interfering cell within range. While downlink trans-
missions are continuously active, the uplink load is typically far lower. With a frame rate
of frames/s, and assuming a maximum uplink rate of transmissions per second per
S/A, a slot is only used with a probability of .%.
•
Multiple interference from the links of more than one adjacent cell. Links from different
cells are mutually asynchronous, causing interference to occur at different times.
(
DL, UL
,UL
,UL
,UL
)
To assess these effects, a generalized cross-correlation was defined and its properties were analyzed.
The results confirm that even in the worst case, the retransmission protocol ensures that messages
canreliablybetransmitted.
28.4 Communication Subsystem Implementation
Figure . shows a WISA base station, which is controlled by a microcontroller. Time-critical con-
trol of the radio frequency (RF) transceiver and baseband signal processing are delegated to an field
programmable gate array (FPGA). The base station maps the wireless links to the addresses of