Image Processing Reference
In-Depth Information
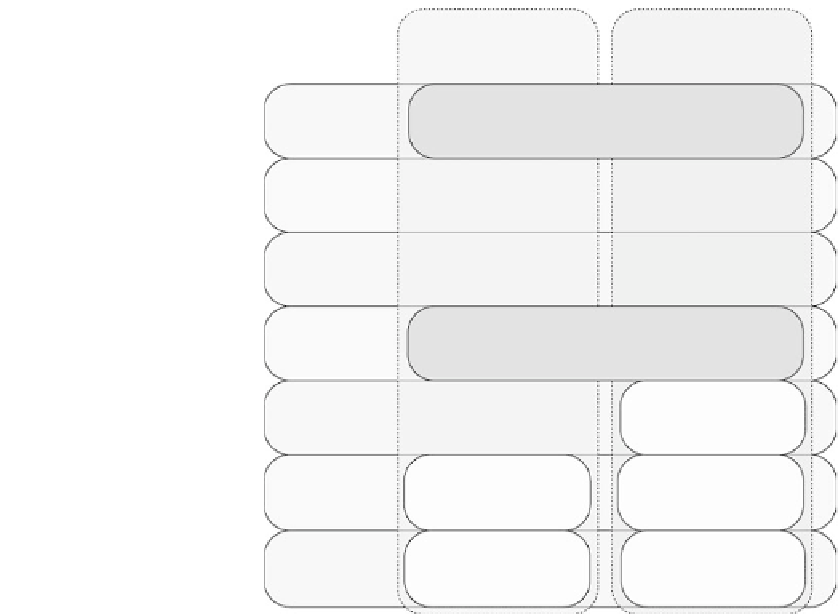
HART
Wireless HART
Layer 7
application
Command-oriented, predefined data types and
application procedures
Layer 6
presentation
Layer 5
session
Auto-segmented transfer of large data sets,
reliable stream transport, and negotiated
segment sizes
Layer 4
transport
Power-optimized,
redundant path mesh
network
Layer 3
network
Time-synchronized,
frequency hopping
protocol
Layer 2
data link
A token passing
master/slave protocol
Simultaneous analog
and digital signaling (4-
20 mA wire)
Layer 1
physical
IEEE 802.15.4-2006,
2.4 GHz
FIGURE .
HART and WirelessHART protocol stacks.
WirelessHART uses several mechanisms in order to successfully coexist in the shared . GHz
ISM band:
•
FHSS
allows WirelessHART to hop across the channels defined in the IEEE ..
standard in order to avoid interference.
•
Clear Channel Assessment
(CCA) is an optional feature that can be performed before
transmitting a message. CCA works like CSMA/CA but without using an exponential
back-off. This improves coexistence with other neighboring wireless systems.
•
Transmit power level
isconigurableonanodelevel.
•
Mechanism to disallow the use of certain channels, called “Blacklisting,” is available.
All of these features also ensure WirelessHART does not interfere with other coexisting wireless
systems that have real-time constraints.
All WirelessHART devices must have routing capability, i.e., there are no reduced function devices
like in ZigBee. Since all devices can be treated equally, in terms of networking capability, installation,
formation, and expansion of a WirelessHART network become simple (self-organizing).
WirelessHART forms mesh topology networks (star networks are also possible), providing redun-
dant paths, which allow messages to be routed around physical obstacles, broken links, and inter-
ference (self-healing). Two different mechanisms are provided for message routing: “Graph routing”
uses predetermined paths to route a message from a source to a destination device. To utilize the
path redundancy, Graph routes consist of several different paths between the source and destination
devices. Graph routing is the preferred way of routing messages both up- and downstream in a Wire-
lessHART network. “Source routing” uses ad-hoc-created routes for the messages without providing