Image Processing Reference
In-Depth Information
Master PSS
Bridges
Cell PSS
I/O block
E-stop
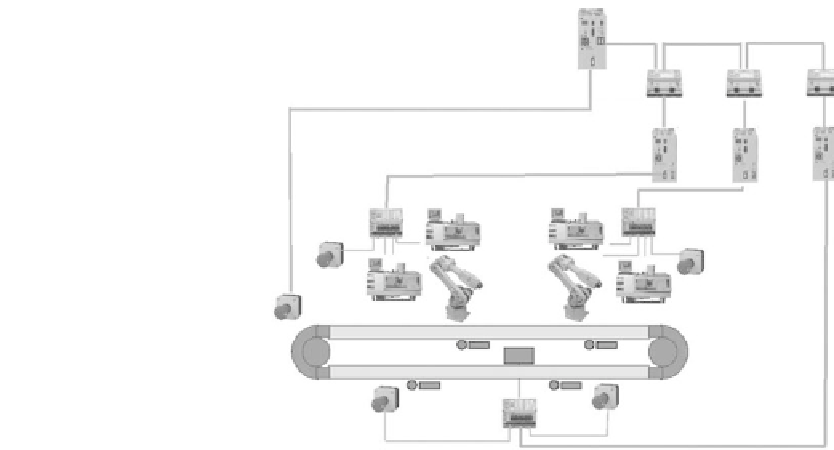
FIGURE .
Safety network implementation on the RFT.
two cells as well as the conveyor. he safety network interlocks the emergency stops, robot cages, and
machine enclosures with the controllers. hese three cell-level networks are coordinated through a
hierarchy to a high-level master safety network. This implementation not only allows for safety at
each cell to be controlled individually, but also provides a capability for system-wide safe shutdown.
Further, this implementation allows for multitier logic to be utilized for the implementation of safety
algorithms.
As manufacturing networks research and development has increasingly shifted toward industrial
Ethernet and wireless communications, so too has the focus in RFT networking deployment and
analysis. For example, in providing an experimental capability to support NCS design evaluation (see
Section .), the wireless performance testbed shown in Figure . was developed in collaboration
with USCAR, a collaboration of automotive manufacturers []. Here, a simple parallel point-to-
point wireless environment is provided for three common industrial wireless protocols: IEEE .,
Bluetooth, and ZigBee. An Ethernet real-time packet “sniffer” is utilized to monitor traffic, thereby
determining the performance of the wireless connection. he testbed is set up so that various wireless
configurations and interference environments can be evaluated in a laboratory setting. The testbed
canthusbeutilizedasbothadesign/evaluationaswellasatrouble-shootingtool.Withrespectto
the latter, wireless signal generation and analysis equipment are utilized with the testbed to effec-
tively “record” wireless patterns in the field and then “play back” these patterns in the experimental
environment for analysis and troubleshooting.
The RFT implementation of multitiered networks for control, diagnostics, and safety provides a
rich research environment for exploration into industrial control networks. Specifically, topics that
can be addressed include () coordination of control, diagnostics, and/or safety operation over one,
two or three separate networks, () distributed control design and operation over a network, () dis-
tribution of control and diagnostics in a hierarchical networked system, () compression techniques
for hierarchical diagnostics systems, () remote control safe operation, () hierarchical networked
safety operation and soft shutdown, () heuristics for optimizing control/diagnostics/safety network
operation, () network standards for manufacturing, as well as () best practices for network systems
design and operation [,,,].